Updated October 11, 2023

Introduction to GIS (Geographic Information Systems)
In layman’s terms, a geographic information system is a system that allows any person or an organization to analyze, store and visualize data related to geographical location. For example, this data can be anything like longitude or latitude, spreadsheets containing address data points, satellite imagery, and admin boundary distribution information. This data is known as spatial data, and databases used to store these kinds of data is called geospatial database. GIS is not just limited to the study of spatial data. Still, it comprises the development, data analysis, editing of data in maps, and even practicing operations – logistics management associated with it.
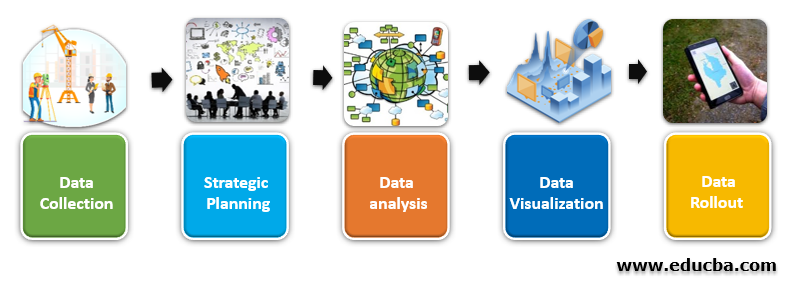
How Does GIS Work?
- Data Collection: Site Engineers and Fieldworkers collect the data using various high-sensor cameras and measurements.
- Strategic Planning: Collected data can be of two types raster images and vector data points such as coordinates. GIS managers and analysts sit together to plan the deliverables.
- Data Analysis: GIS analysts, developers, and technicians work with the architects to deal with the analysis and the analytics part of the work.
- Data Visualizations: GIS Technicians and Analysts, with the help of BI consultants, work on the byproduct of the visualizations post-processing and analysis of spatial data.
- Data Rollout: The final product is then rolled out to the end consumers and strategic partners/costumers with recently updated mapping and navigation Info. Consumers also have the option to report back to work with various feedback and comments.
Features
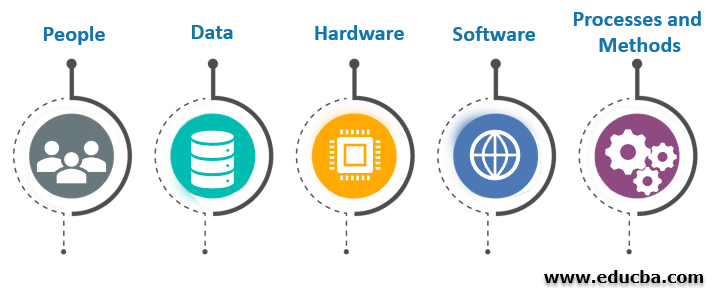
A working Geographic Information System comprises 5 crucial components.
They are as follows:
People, Data, Hardware, Software/Applications, and Methods.
The above Infographic is added to showcase the general components of GIS in an interactive image format.
1. People
This is one of the important factors in Geographic Information Systems. This technology will be handicapped without this component. It ranges from the people working on complex geospatial databases to the consumers who use maps daily.
2. Data
Collecting and managing accurate spatial data is the most valuable and essential component in setting up any GIS. Primarily it is classified into vector and raster data. Vector data is all about coordinates and shapes. However, raster data is all about satellite imagery sources. Organizations and institutions also use cloud and Database Management Systems to manage geospatial data.
3. Hardware
Hardware is also crucial to managing geospatial data and complex software to set up Geographic Information Systems. It can be standalone, virtual, or network-driven, depending on the volume of data.
4. Software
The hardware complements the software part of the system. The software comprises query building and handling tools, Database Management Systems to store the geospatial data, an Input and edit tool to manipulate geospatial data, and a Graphical User Interface to easily access the geospatial data from the front end. ESRI is a giant that has ArcGIS to its name. Some organizations also have their proprietary software. Open-source software like QGIS is well-known among students and beginners in GIS.
5. Processes and Methods
Geographic Information Systems need proper planning and approach. It’s not an overnight task to build a good system. Indeed there are many set processes and methods that organizations need to follow. Organizations like HERE MAPS use the LEAN and kaizen methods to keep the data quality and system top-notch.
Applications of Geographic Information Systems
Advantages and Disadvantages of GIS
Below are the advantages and disadvantages :
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
| It can process multiple data formats and data sets. For example, Satellite images and vector data points like coordinates, latitude, and longitude drive files from drones and high-sensor cameras. | GIS often requires trained candidates from Geology, bioinformatics, or Information technology. Non – GIS person will end up ruining the setup entirely. |
| GIS can be integrated with various hardware and software to create a robust environment. | It is incomplete without the available meaningful spatial datasets and databases. |
| This system can analyze past data sets and analytics on future predictions based on the trends. | People and organizations complain about GIS being very expensive to implement and integrate. |
| It is used for natural resource management by analyzing, managing, and monitoring natural hazards. | It requires a large amount of data to be inputted into the system, and hence, there are more chances of errors. |
| It is highly efficient for data collection, processing, and visualization. | Most of the time, organizations fail to implement fully functioning GIS. |
| It allows easy record-keeping of geographical changes for further analysis. | Data privacy and integrity is an essential asset of GIS. It has more risks when it comes to privacy violations. |
Career Growth in GIS
- Working in the field of GIS is more than data analysis and operating GUI-based software. GIS nowadays is evolving more than what was defined in textbooks and universities.
- The job roles in this domain are becoming more advanced with the amalgamation of data analysis, programming, backend technologies, and even geography knowledge. With data science and Machine learning /AI booming the market, the organizations also integrate ML / AI-based models in the systems to improve prediction and accuracy. Many universities offer Geo-Informatics and GIS as the main elective in their programs.
- Product-based companies like HERE Maps, Bing Maps, Google Maps, Apple Maps, TomTom, and ESRI are coming out with many job roles and responsibilities for upcoming graduates. Service-based companies like Capgemini Technologies and Willis Tower Watson use GIS for cartographic models to identify potential risks.
- Roles include GIS technician, Analyst, spatial analyst, GIS data specialist, GIS developer, and Architect. GIS Technicians work on the GUI-based GIS software to build maps. GIS Analysts and Spatial data analysts work on the spatial data that is available and extracted through various sources.
- GIS developers and architects work with database engineers to build a robust GIS. The architect is the one who creates the whole architecture, and this whole project or program is orchestrated by a GIS Project or a Program manager.
- Companies like HERE are working on automobile navigation and advanced driving assistance systems. A famous consortium of Daimler, BMW, and Audi funds the organization.
- They are also integrating various maps with drone companies like DJI.
- Apple and Google mostly work on the lower consumer crowd for desktop, phone, and tablet experiences. TomTom is always a frontier in the field of GPS devices. They have various navigation devices to their name.
Conclusion
Many organizations and people always underestimate the power of this system. They think it’s an expensive setup with less ROI. However, companies and people who have mastered this domain are thriving in the market with abundant success. Companies like HERE Maps, Tele Atlas, Apple, Bing Maps, and TomTom are fighting against tech giants like ESRI and Google. GIS will always have immense investment, but the organization investing in this will reap the benefits if things are planned properly.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to What is GIS? Here we discuss the introduction, features, working, applications of geographic information systems, and advantages and disadvantages. You can also go through our suggested articles to learn more –