Introduction to Hub
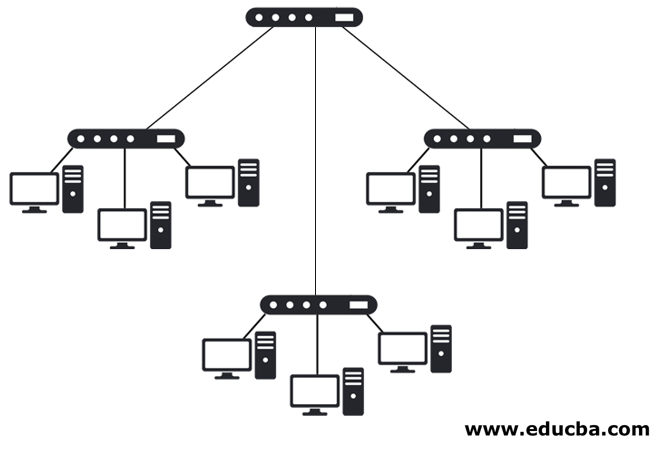
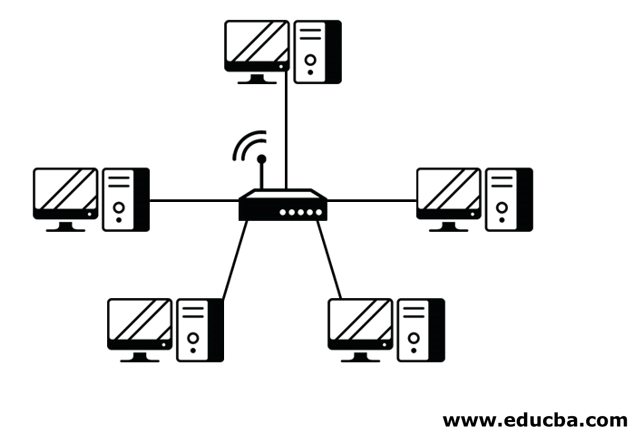
A hub is a network hub used for the connection of devices in a network. It connects several devices in a LAN. All the network connection devices are connected through a hub that acts as a central connection for all the devices. There are many ports in it, and if a packet arrives only at one port, it is copied so that all the ports can see the packets. This helps if there is any trouble in one port of the hub. The three types are active, passive and intelligent. Active hubs amplify the incoming electric signal, whereas passive hubs do not amplify the electric signal. Intelligent hubs are kind of active hubs.
What is the Hub Network?
The network hub is an interface connecting physical devices such as a printer, I/O devices, desktop, storage devices and all servers in the data center. It is according to the requirement or plans to choose the configuration of the hub. It plays the main role in a star topology. If the user is implementing a T-shaped network, they connect their devices, where there is no point in using it since they have only two systems.
Types of Hub
There are three types that are deployed according to their usage. They are passive, active, and intelligent. In recent days, the modification was done to hubs that provide high performance.
1. Passive Hub
- It has quiescent creatures as the name portraits, and it does not impact performance, but it helps identify the bugs and detect the faulty hardware. They are a simple that receives the packet on a port and is then broadcast to all the port.
- It has a 10base-2 port and RJ-45 connectors, which is connected to each local area network device. This connecter is applied as a standard one in your network. AUI ports are placed in advanced passive hubs, which are connected as the transceiver as per the network design.
2. Active Hub
- They have some additional features apart from passive hubs. It monitors the data which is sent out to the connected devices. It has a unique role in this network communication by using Store technology to check the data before sending it out and prioritising which packet to send first.
- It has the option to fix the damaged packets and hold the direction and distribution of the rest of the packets. If a week signal is received in port, but it’s still readable, then the active hub amplifies it to a stronger signal before its retransmitted to other ports.
- If any connecting device is not functioning in the network, it can boost the signal, which other devices view with passive hubs. Hence it helps in the continuation of service in the local area network.
- But few of them will account for the malfunction of any device and offer related diagnostic capabilities in the local area network. They will be able to resync the packets and transmit them again. Some cables go through electromagnetic troubles and stop the packet from entering into the designated port, or rarely it does not reach the port. At those times, they can make up for the packet or data loss. They are accessible to retime the port for slower delivery and error-prone connections.
3. Intelligent Hub
- These give many advantages than passive and active hubs. The management who wants to expand their business in networking can assign users to share a common pool efficiently and work more quickly using intelligent hubs. The technique behind them is explored recently, and now its great demand in the market.
- It is proved that it delivers unparallel performance for your local area network. If any problem is detected with any physical device, it is easily detected, diagnosed, and solved using management data that the hub can rectify.
- This is a standard improvement over active hubs. Detecting the centralized management tool helps to explore the network that runs out of the device to find the low functioning devices.
- Another feature is flexibility which has high transmission rates to numerous devices. They have their standard terms with transmission rate as 10, 16, in the speed of 100Mbps to desktop.
Benefits
- The technical information has a physical layer function which is connecting multiple hubs and has numerous benefits. They detect crucial problems and immoderate collision and interrupt jabbering occurred between ports or devices. If any fault occurs, it disconnects the signal flow and prevents the damaged device from the rest of the device.
- If there is any misbehavior or hissing in a cable can also be detected and prevented the device from great loss. It has an inbuilt twisted based ethernet which helps to detect any malfunction. To pass the data through each segment through the repeater should be the same in all partitions because the repeater cannot connect the data with different segments.
- Many classes have varied speed range hubs. Class 1 has a signal delay of 140-bit time by setting a transaction record in a range of 100BASE-TX, and 100BASE-T4 whereas class 2 has a signal delay of 92-bit time by accessing a single collision domain.
- Dual speed is an internal port switch that works on 10M/bits and 100M/bits segments. When any device is connected with these segments, the port becomes active. The data signal is transmitted at a higher rate, but this turns into a failure model because it fails to design the switch between traffic flow.
Conclusion
A switch is part of Hub, which tracks all details of the connected devices’ MAC address. It knows about the system or devices and their connection port, so if any packet is received, the switch chooses and sends it to that port. The network hub is also called an active multiport repeater, ethernet, and repeater. The hubs and switches with multiple inputs and output ports that form a network, and all the connected devices act as a single network segment and work efficiently, preventing data loss.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to What is Hub?. Here we discuss the basic concept, three types of the hub, which is deployed according to its usage and the benefits. You may also look at the following article to learn more –