Updated March 13, 2023

What is Hypervisor?
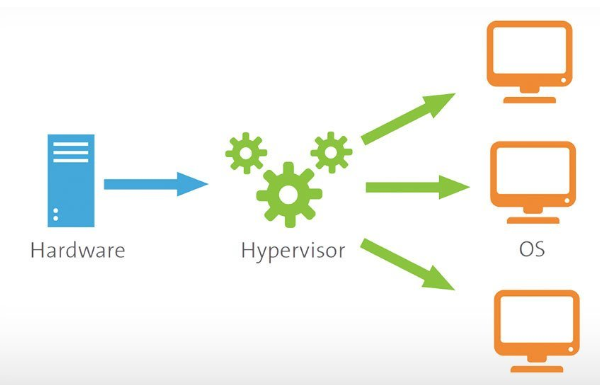
The word hypervisor is derived from the supervisor who is a traditional term for an operating system’s kernel. It is a process or function that can isolate the applications and operating system from the underlying computer hardware. It allows the abstraction, and thus a host machine hardware can independently operate one or more virtual machines as a guest; this allows the guest Virtual machines to effectively share the system’s resources such as memory, network, processors, etc.
The virtual machine monitor known as VMM creates and runs the virtual machine (VM) instances. It can be software, firmware or hardware that hosts the VM instances. There are two categories available: Type 1 hypervisors or Bare Metal and Type 2 hypervisors or Hosted. The Bare Metal runs directly on the host machine hardware. The Hosted are the software versions of hypervisors that run on the Operating system. It helps to isolate the VM OS and applications from the underlying host hardware and software through vitalization. Some of the popular are VMware Server and Oracle VM.
There are mainly two types of it.
- Type 1 hypervisors or “Bare Metal”
- Type 2 hypervisors or “Hosted”
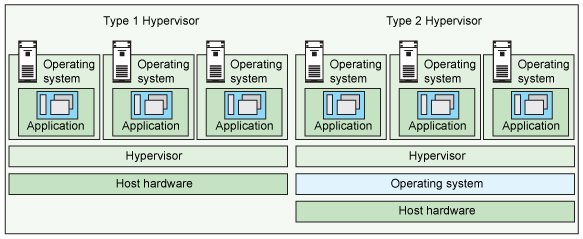
Type 1 is the one that runs directly on the host’s hardware; type 2 is the one that runs as a software layer on an operating system.
The first-ever hypervisor which provides full virtualization was the SIMMON, a test tool developed by IBM in 1967.
The figure above depicts a typical functioning where it runs multiple guests on a host.
Understanding
So far, we have discussed on a very high level what it is; let’s go in deep and see what we can do with the hypervisor and the different types. As stated earlier, there are mainly two types of it, i.e. Type1 and Type 2.
Let’s see the difference between both of them.
Type I Hypervisor
This type runs directly on an underlying host system. It does not require any operating system as a base server. It has direct access to hardware resources.
Examples of Type 1 are VMware, Citrix, ESXi, XenServer, and Hyper-V hypervisor.
Let’s see what their different features are:
1. VMware ESX & ESXi
VMware is the leader in providing Type 1; they have advanced features and scalability. These kinds of hypervisors incur licensing fees. VMware also offers some low-cost hypervisors best suited for smaller infrastructure.
2. Citrix XenServer
Like VMware, Citrix also offers both free and commercial products. The product having basic technology is free and does not have any advanced features.
3. Oracle VM
Oracle VM lacks many advanced features which VMware offers; it is very similar to open source Xen. The basic version is free; however, for the support and the product updates licensing fee is applicable.
Type II Hypervisors
Let’s see at Type II Hypervisors:
1. VMware Workstation & Player
VMware Player is free to type II offers by VMware; it can run only one Virtual Machine and does not allow multiple guests. VMWare workstation has many advanced features like VM snapshot, record, and replay, etc.
2. VMware Server
It is very similar to the VMware workstation and provides hosted virtualization hypervisor. However, VMware has stopped the development since 2009
3. Microsoft Virtual PC
It runs only on Windows 7 & above, and this is the latest Microsoft version hypervisor technology by Microsoft. It only offers Windows operating systems.
4. Red Hat Enterprise Virtualization
This is a kernel-based virtual machine and has qualities of both Types I & Type II. Here the VM has direct access to the physical hardware as the Linux kernel turns into hypervisor itself.
How to Choose the Right One?
Now that we have covered both types of Hypervisor and different vendors and their product, which offers Hypervisor, you must be thinking about making a decision on the right hypervisor that best suits your need. If you are thinking the same, then you are on the right track. Let’s see how can you choose the right Hypervisor. Before evaluating the pros and cons, it’s very important to first analyze the need of the Hypervisor.
Why do we Need it?
It is the need for any system administration or system operator. It allows virtualizing the storage resources to create a centralized storage pool for the admin to provide provision without any concern where the storage is located physically. Networks can also be virtualized with Hypervisor; it allows the network device to be created, managed, or changed without any concerns of having the network devices’ physical location. In short, we need it to efficiently utilize the infrastructure, provide reliable support, and improved application scalability.
Now that we have seen the need for it, let’s see the various factors that you should consider before choosing it.
Type I performs better than Type II.
Generally, Type I provides better performance than Type II as it does not have any middle layer making them ideal for projects where speed is a concern.
Type II on the other side is much simpler to host and set up. In order to determine which best suit the project’s needs, you can compare the performance metrics. This encompasses guest memory, CPU overhead, maximum host. Also, the virtual system should be better or equivalent in performance to its physical counterparts. The other important parameter to look for is the licensing fee for the product and the support. Though many entry-level products are free, they don’t offer any advanced features. Thus it’s important to strike a balance between the licensing cost and the features.
Conclusion – What is Hypervisor?
Now that we have reached the end of the article, I hope you guys have a fair idea of what it is, what are the different types, why do we need them, and how to select the right one as per your need. This is a very high-level discussion on it; if you want to understand any specific product, their licensing cost, and the offered services, you can go to the respective vendor’s website.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to What is Hypervisor? Here we have discussed the basic concept, need, types of hypervisor with their features, and how to choose the right one. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –