Updated March 15, 2023

Overview of What is Man in the Middle Attack
Man in the middle attack is also called a bucket brigade attack, occurs when some unauthorized person gets access to the authorized message or data, which is a transfer from sender to receiver or vice versa. For example, suppose user A wants to communicate with B, A sends 3 as a value to B, the attacker present in between A and B gets access to the value of A and changes it to 9 and sends 9 to B. In other words, we can say that when the attacker sits between the sender and receiver and modify the data transferred between them is called Man in a middle attack.
Man in the Middle Attack
When two users are communicating with each other, another third unknown entity enters into the conversation to eavesdrop to attain the data from the conversation. This third unknown entity is totally unknown to the recipient and sender of the communications (users). E.g., You are chatting with someone online. There’s a third unknown entity present in the communication, which is totally unknown to both of you. This third person might chat individually with both in a way that both will keep thinking that the other is sending messages. Or the third entity can intercept the messages and add new content to them. This all will be done so discreetly that both the users will remain totally un-notified.
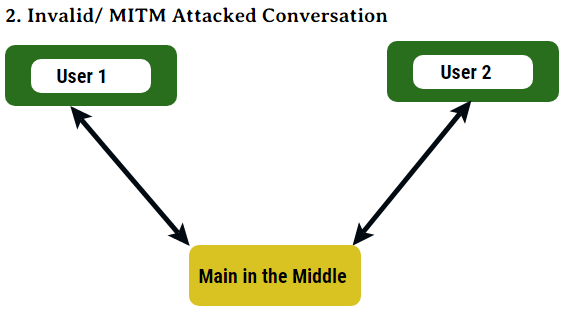
The following diagrams depict how a MITM happens:
Figure 1: This is the regular route or the channel through which the communication should take place.
Figure 2: The communication is taking place through the altered channel, and Man in the Middle has attacked the systems /users.
In simple words, Main in the Middle Attack is the same as the person who eavesdrops in the conversation and uses the information for his/her benefit.
Types of Man in the Middle Attack
Below are the different types of man in the middle attack:
1. Session Hacks
We often get notifications when we browse about cookies and sessions. So these cookies and sessions store the information which is our personal. For example, it might contain login ids and passwords. So what MITM attackers do is they get the hold of these session cookies, and once they have it, all the sensitive data is accessible to them, and then the data theft happens. Generally, all the sites have auto-fill up forms, ask users to enter the passwords and verify, etc., this is where they get people’s data.
2. Email Hacks
MITM attackers access the interception of messages between two users. The first user sends some sensitive information over the net to the second user. So, it works exactly like figure 2. The attacker sends the email to either party, which is masked, which means either one doesn’t figure it out that it is fake and demands some sensitive information or account details, and then the hacking takes place.
3. Wi-Fi Hacks
Generally, this happens when users connect to a free Wi-Fi source, and hackers can easily target such users. Free Wi-Fi sources are crucial mediums of connections, as a very low-security level is made available through it. Another Wi-Fi hack is, the attackers develop a very similar network to what the users are currently working on.
Purpose & Motive of Man in the Middle Attack
Man in the Middle attackers; generally target the users who are naive with the network controls. Easy targets. But, it doesn’t mean that complex systems cannot be hacked. These attackers gather this information and then use it as a normal user to use it. It is mainly targeted to get sensitive information of/from the users like account details, bank PINs. This information helps them to enter into the system and use it or even sell the information. This has been seen recently many times, that due to the attacker, system data has been published online or sensitive data has been leaked.
How does Man in the Middle take Place?
There are two main steps with the help of which MITM attackers hack into the systems; viz:
1. Interception
The attacker makes a dummy network that users can use for free. And when the users enter the data, it is first transferred to the attacker’s files and then towards the reallocation. This is the passive and most easy of attacking the systems.
Attackers might use one of the following ways too:
- IP Spoofing: All the devices have IP addresses. When the user enters the data over a network, it gets transferred to the receivers IP address. But in between, the attackers create some IP addresses which are very similar to the recipient’s IP address. So, instead of sending data to the real destination, it gets transferred to the attacker’s IP address.
- ARP Spoofing: In this, MAC addresses of the attackers are attached along with the user’s IP address. So data gets transferred to the attacker’s IP address as soon as it is sent.
- DNS Spoofing: DNS means Domain Name System. Attackers, change the cache records of the browsers. So when the user enters the given site, instead of going to the correct URL / website, it is sent to some dummy site that the attacker has created.
2. Decryption
- HTTPS Spoofing: Generally, all the users see the “https” as secure. But in this attacker puts in manually a certificate, which looks like secure and trusted to be used. So, all the data is routed through it. But as it looks similar to a secure site, the browser sends the key to read the data; an attacker gains access to the information.
- SSL Beast: The attacker infects the user’s computer with some false cookies, and CBC is compromised, so the data is easily decrypted.
- SSL Hijacking: As mentioned earlier, HTTPS stands for secure. Just before the browser connects to the HTTPS from HTTP, it is routed to the attacker’s browser.
- SSL Stripping: Attacker brings down the website security to a level where all it is in between HTTPS and HTTP. So all the data is available in a non-encrypted textual format.
What to do after Man in the Middle Attack and How to Prevent it?
There are certain ways/steps which can be followed to prevent the attack after it has taken place, viz:
- Check the security levels of the networks with which you are connected with.
- Never connect to the Free Wi-Fi source unless it is from a known source.
- Stay alerted of potentially fraudulent emails and unknown links, which might lead to other unknown websites.
- Stay connected to the websites connected with HTTPS protocols; they have more security levels over HTTP.
- Use VPNs while on a network, so the data which is being used or transferred securely. All the data is fetched and saved using a VPN is encrypted.
- Use anti-malware software that detects and eliminate malware.
Conclusion
While using data on the network, always stay connected to the secure sites and avoid clicking on the links, leading to some unknown sources.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to What is Man in the Middle Attack. Here we discuss the overview, types, purpose & motive etc. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –