Updated August 10, 2023
Introduction to Router
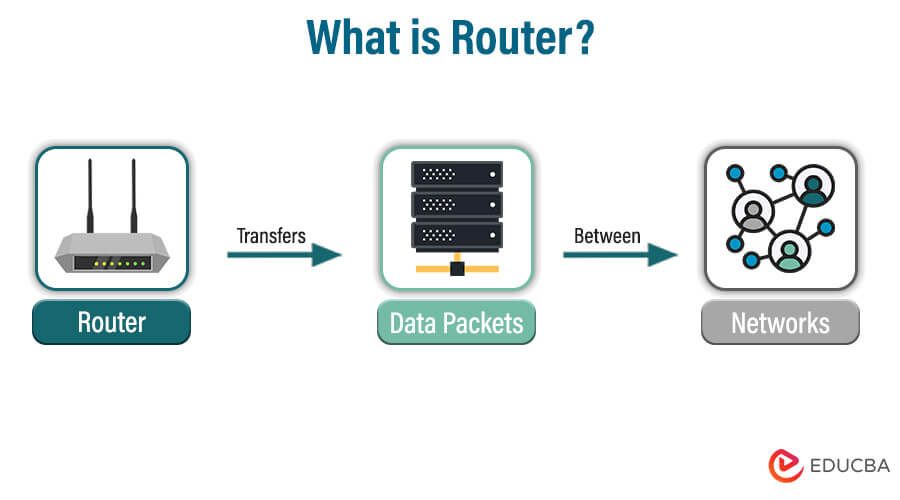
A router is used to transfer data packets between networks. Data from the internet is always sent through packets, and routers perform the function of directing traffic to different networks in the computer. There should be at least two networks within which the router is connected, i.e., two LANs or a LAN and a WAN. Most routers are placed at gateways where the networks are connected. There are wired, wireless, core, edge, and virtual routers available. Routers usually select the best route to direct the packets to reach faster. The best example is the mail carrier.
Are you looking for a reliable router to keep your home or office connected
Top 5 Types of Router
Below are the different types of Router:
1. Wireless
It is present in the office, home, railway station, etc. It creates a wireless signal. Suppose you are in the office; you can connect to the internet using wireless signals because your laptop is within range. We can provide security to routers by entering user IDs and passwords. When we try to connect to the router, it will ask for a password and UserId. User ID and password come along with the device. Due to security, no information about the user is harmed. When we visit public places, we can observe that a Wi-Fi window will prop up to use the internet on our phone and that it is secure with a password. Wireless routers are publicly available. N number of users can connect to it.
2. Wired Router
The name itself defines its meaning. A wire is available to connect to the network. If we visit a bank, small college, or office, we can observe that a PC or laptop connects to the internet using an Ethernet cable that it plugs into a wired router. It has a separate Wi-Fi access point. Users can use VOIP (voice-over IP technology) to connect to the phone. An ADSL (modem) has two jacks to connect to ethernet and mobile phones.
3. Edge Router
It sits at the edge of the network’s backbone and can connect to the core routers. A router can be wired or wireless, and its purpose is to distribute internet data packets between one or more networks. But it will not distribute internet data packets within networks.
4. Core Router
It is designed to operate in the internet backbone or core. Also, it supports multiple telecommunication interfaces of the highest speed and usage in the core internet. It can forward IP packets at full speed on all of them. The router supports the routing protocol used in the core. It will distribute internet data packets within the network. But the core will not distribute internet data packets between networks.
5. Virtual Router
It is the default for a computer-sharing network. It functions per the virtual router redundancy protocol (VRRP) and becomes active when the main or primary router fails or becomes disabled. However, it takes multiple routers in a group to share a virtual IP address. It has a master for each group that handles IP packets. If the master fails while forwarding packets, other routers will take a position.
Features of Router
Below are the features:
🔧 Wireless Routers: Wireless routers are a great choice for those who want to stream movies, play online games, and stay connected from anywhere in the home.
🔩 Modem Routers: Modem routers are a great option for connecting multiple devices to the internet.
🔌 Mesh Routers: Mesh routers are perfect for those who need to cover a large area with Wi-Fi.
💻 High-Speed Connection: Enjoy a high-speed connection with this router that allows you to stream, browse, and game easily.
🔒 Security: Equipped with the latest WPA2 security protocol, this router ensures your secure connection.
🔋 Long-lasting Battery Life: This router features an impressive battery life that allows you to stay connected for hours without recharging.
Specifications
– 802.11a/b/g/n/ac wireless connectivity
– 5GHz and 2.4GHz dual-band support
– 4x Gigabit Ethernet ports
– Range: 300ft
– Speed: Up to 300Mbps
Benefits of Router
Below are the benefits of the Router:
- The collision feature can reduce network traffic.
- Broadcasting domains can reduce network traffic.
- It provides a MAC and IP address that will choose the best route across a network.
- Easy to connect to the wired or wireless network.
- Highly secured with a password.
- No loss of information.
- It can connect to network architectures such as ethernet cable, Wi-Fi, and WLAN.
- The wireless router is easy to connect to the internet for a laptop or pc. No need to worry about a bunch of wires.
How does routing take place?
When a packet is introduced into the network and received by one of the routers, it reads the packet’s headers to understand the destination. It checks its routing table marked with its metrics to see what would be the next best hope for the packet to reach the destination optimally. Then, it pushes the packet to the next node, and the above process also repeats at the new node until the packet reaches the destination node.
Routing metrics
These tables have information on which packet switching takes place in the most optimal path. And this information is different metrics or variables the routing algorithms look for and then decide their path. The standard metrics include the following –
- Path Length: The administrator will assign costs to each path (between two nodes). The path length will be the sum of all the path costs. The path with less length will be chosen as the most optimal one.
- Delay: This measures the time it takes for the packet to route from source to destination. This depends on many factors like network bandwidth, the number of intermediate nodes, congestion at nodes, etc. Sooner the transfer, the better the Quality of Service (QoS).
- Bandwidth: This refers to the amount of data a link can transfer through it. Usually, the enterprise lease the network line to achieve a higher link and bandwidth.
- Load: Load refers to the traffic a router or a link handles. The unbalanced or unhandled load might cause congestion and a lower rate of transmission packet losses.
- Communication Cost: This is the operational expense that the company incurs by sending the packets on the leased line between the nodes.
- Resilience and Reliability: This refers to the error-handling capacity of the router and the routing algorithms. If some nodes in the network fail, then the resilience and reliability measure will show us how well the other nodes can handle the traffic.
Types of Routing
There are two types:
1. Static Routing
This type is the optimal path between all possible pairs of sources & destinations in the given network, is predefined, and fed into the routing table of the network’s routers.
Advantages
- There is no CPU overhead for the routers to decide the next hop for the packet as the paths are predefined.
- This offers higher security as the administrator has autonomy over packet flow permissions along a defined path.
- Between the routers, no bandwidth would be used (for tasks like updating its table, etc.)
Disadvantages
- It will be difficult for the administrator to identify and predefine an optimal path from all possible combinations of source & destination nodes for larger network topology.
- The administrator would be expected to be thorough in the concepts of networks and topology. Transitioning to a new administrator would consume time in understanding the topology and defined policies.
2. Dynamic Routing
This type allows the router to discover the network by protocols like OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) and RIP (Routing Information Protocol), updates the routing table by itself, and effectively decides upon the path that the incoming packet must follow to reach its destination.
Advantages
- This is easy to configure.
- It would be efficient to discover some remote networks and execute routing there.
Disadvantages
- When one of the routers in the network implementing dynamic routings discovers change or generates an update, it broadcasts it to all the nodes. Thus, consuming a higher amount of bandwidth.
- It is relatively less secure than static.
Types of Routing Algorithms
There are two types of algorithms:
1. Adaptive
The routes are decided dynamically based on the changes in the network topology.
- Distance Vector Routing: In this algorithm, each router maintains an entry for each router in the network. This is called the Bellman-Ford Algorithm. Initially, this was the ARPANET algorithm.
- Link State Routing: LSR discovers the neighbors, measures the cost to each neighbor, then constructs the packets and sends them along the computed shortest path.
2. Non-Adaptive
The routers decide the routes statically.
- Flooding: In this, you send the packets to every other neighboring router & they turn to the same, and by some path, the packet reaches its destination. This duplicates the packets, but the reliability is very high in routing. Defense networks, distributed databases, wireless networks, and routing tables primarily utilize this method.
How will this help in your career growth?
The network architecture in data centers, telephonic lines, cloud clusters, etc., is crucial for businesses to run. Telecommunication companies, Computer Network companies work day in and day out to come up with better network routing algorithms and routing protocols, to have the network virtualized, enhance the network security by designing secure network protocols and encryption techniques, achieve higher resilience, and provide better & faster quality of service. With such an overwhelming scope in the domain, pursuing one’s career in Computer Networks is excellent.
Conclusion
We have learned that a router is a hardware device that moves, analyzes, and receives internet data packets within a network. It has more network functionalities than a hub or switches. We can keep the PC safe from an attacker because of the firewall and the router’s enabling security. The manufacturer should update the firmware software.
FAQ
Q: How long does the battery last?
A: The battery life of this device is up to 8 hours.
Q: How fast is the connection?
A: This offers up to 1.2Gbps speed.
Q: Does this have dual-band Wi-Fi?
A: Yes, this features dual-band Wi-Fi.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “What is Router?” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.



