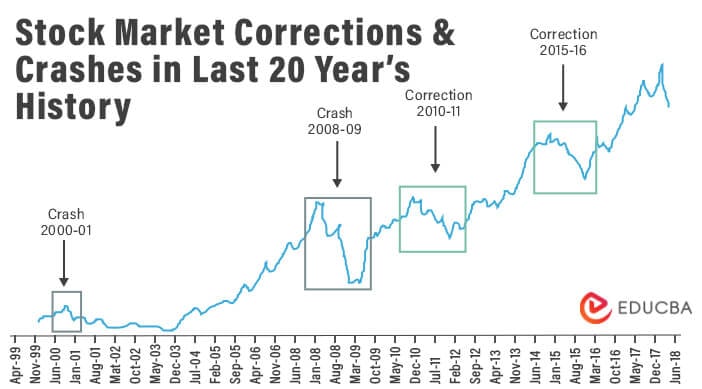
What is Stock Market?
The stock market is a space where individuals can trade shares and securities of public companies. It is a group of financial institutions and agents dealing with asset classes, including bonds, shares, funds, etc.
The trading occurs using specific stock market instruments, like mutual funds, ETFs, etc. A company can trade its own stocks to incentivize people within its management or invest in a new project.
Key Takeaways
- The stock market is a worldwide network of people, companies, and information where one can purchase and sell shares of publicly-traded companies.
- Among its various functions, healthy investments, balanced regulation, reputable trading, and maintaining liquidity are a few.
- The instruments are financial tools that allow investors to buy and sell stocks. These include shares, bonds, mutual funds, and more.
- The stock exchanges, regulatory bodies, traders & brokers, and issuers are prominent market participants.
- Using financial ratios to analyze stocks is a beneficial strategy. Apart from the crucial P/E ratio and the dividend yield ratio, investors should also know the EPS, PEG, Debt-to-equity ratio, etc.
History
- The idea for the stock market began in the twelfth century due to the mismanagement of debt securities.
- The Italians were the first to start informal market meetings, which soon spread over the neighboring countries.
- In the 13th century, bankers initiated trading in government securities. However, the introduction to the concept of stocks as a form of investment did not happen until the 16th.
- Starting in 1602, the Dutch East India Company became the first public company to sell its shares.
- The trades began occurring at the Amsterdam market. Other derivatives, like bonds and options, were added along with shares.
- A merchant group started conducting meetings to buy and sell stocks in the late 17th century. That was the beginning of the New York Stock Exchange.
- Soon people formed another stock exchange named Philadelphia Stock Exchange (PHLX).
- Approximately two centuries later, the National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations (NASDAQ) acquired PHLX.
That’s how the stock market got its start. It has evolved, but one thing remains true: it can provide excellent opportunities for financial security as long as people invest carefully.
How Stock Market Work?
The stock market trades shares, which are pieces of ownership in a company. Regulatory bodies like the SEC, SEBI, etc., regulate market operations. Simply put, these markets provide a safe environment for participants to confidently trade financial instruments with zero/low operating risk. They function as primary and secondary markets.
a) Primary Market
- In a primary market, companies can issue and sell shares to the general public for the first time. It is known as the initial public offering (IPO).
- This activity assists businesses in obtaining the necessary capital from investors.
- It divides the company into several shares (e.g., 20 million) and sells a portion of those shares to the general public at a price (e.g., $10 per share).
- The stock exchange facilitates this capital-raising process. It compensates by charging the company and its financial partners for the services.
b) Secondary Market
- After an IPO company lists its shares, the stock exchange is a trading platform that facilitates regular buying and selling. It is called the secondary market.
- Individuals can choose a stock during the secondary market activity and start trading.
- When the trader wants to buy, they need to offer a bid price; when they want to sell, they have to set an asking price.
- Most of the time, there is a vast difference between the prices, known as the bid-ask spread. Thus, the seller, the buyer, or both make the compromise.
- Many traders choose brokers to trade on their behalf to make the process easier.
Functions of the Stock Market
1. Reputable Trading of Securities
It makes sure the participants have immediate access to information regarding all buy and sell orders. It is the fundamental law of demand and supply, assisting in securities’ fair and open pricing. Additionally, they effectively support the mechanism to match appropriate buy and sell orders.
2. Maintaining Liquidity
It provides access to anyone qualified and willing to place orders. The dynamic setting ensures the investors that they can liquify their investments anytime. It instills a sense of reliability and confidence in the market.
3. Security and Validity of Transactions
The market requires participants to operate efficiently, but they should also certify all participants. The people trading should be verified and follow the necessary rules, leaving no room for non-compliance by either party. Additionally, associated businesses operating in the market should abide by the laws and regulatory framework.
4. Balanced Regulation
Market regulators, like the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission, keep an eye on publicly traded companies’ transactions and have significant regulatory authority over them. They also impose quarterly financial reporting and immediate notification of pertinent developments.
5. Economic Growth
It can be helpful to analyze the economy of a country. Falling stock prices can indicate a downturn and vice versa. It also enables growth in the economy through the constant flow of capital. Cash flow increases as thousands of investors invest and liquefy simultaneously, leading to economic growth.
6. Healthy Investments
These markets empower people to make more investments. With numerous instruments and opportunities, it generates a row of effective investing habits. Additionally, as people speculate on the market and put money in for profits, they choose up-and-running companies. This way, successful companies survive and grow with their investments.
Examples
Download the Excel template here – Stock Market Excel Template
Example #1
Let us take an example of the primary market.
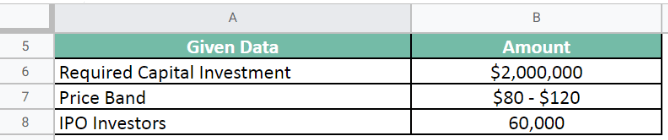
Company XYZ launches its IPO in the market. It is looking to raise a capital investment of $2,000,000. In the issue details, the company announces the price band of each share as $80-$120. It sets a 3-day gap between the open and close date. During the dates, a total of 60,000 individuals invested in the IPO.
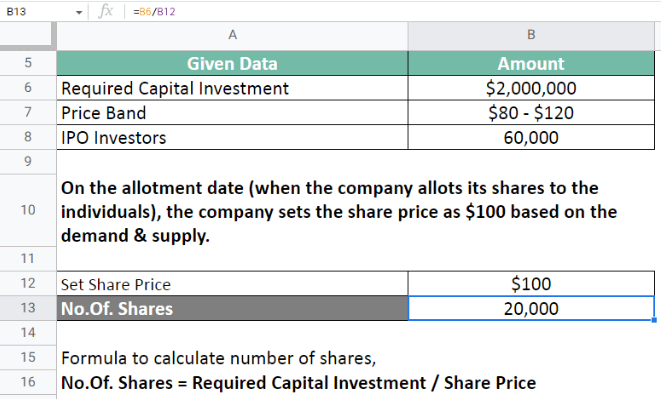
On the allotment date (when the company allows its shares to the individuals), the company sets the share price as $100 based on the demand & supply.
Therefore, the number of shares is 20,000.
As there are 60,000 investors, a lucky draw takes place to aid the allotment process. Through which 20,000 investors get the respective shares.
On a listing day, the company’s shares are allotted and listed on the secondary market for all traders to trade in.
Example #2
Let us take an example of the secondary market.
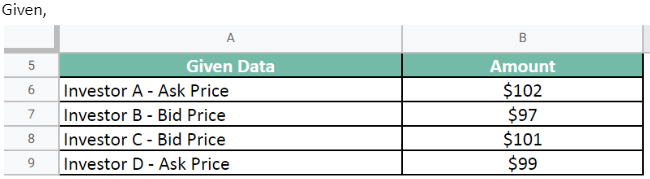
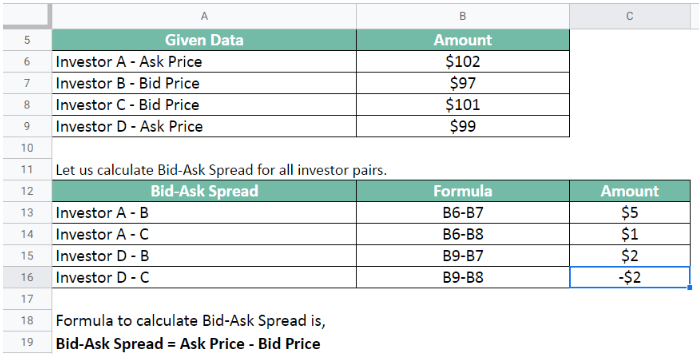
The company XYZ has listed shares in the market. There are 4 investors looking to sell and buy a stock of the company simultaneously.
- Investor A wants to sell the share at an asking price of $102
- Investor B wants to buy the share at a bid price of $97
- Investor C wants to buy the share at $101
- Investor D intends to sell the share at $99.
Calculate the bid-ask spread and match the buyers and sellers.
Let us calculate Bid-Ask Spread for all investor pairs.
The favorable bid-ask spreads for the investors are between Investors A & C and Investors D & B.
Therefore, after making a few compromises,
A can sell the share to C; B can buy the share from D.
That is how the secondary markets usually work.
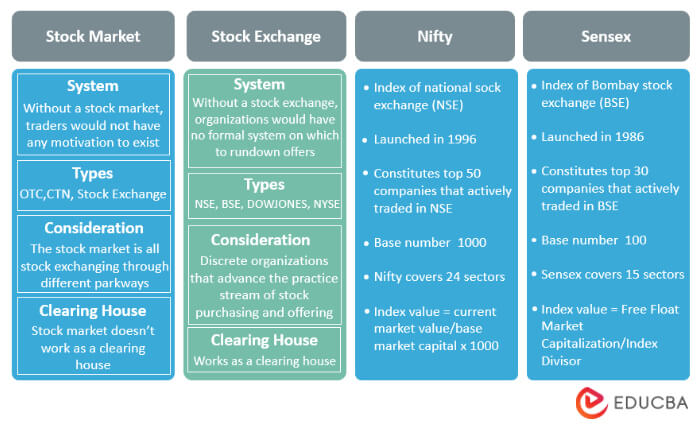
Stock Market vs. Stock Exchange vs. Stock Indexes
Stock Exchange
- Historically known as a bourse, it is a place for trading securities such as stocks, bonds, and options contracts.
- The trade for various companies’ shares happens on this platform.
- Some exchanges are the New York Stock Exchange, Frankfurt Stock Exchange, Hong Kong Stock Exchange, etc.
Stock Market
- It is generally a group of the country’s stock exchanges.
- The market enables traders to trade across different stock exchanges.
- For example, the Indian stock market includes the Bombay Stock Exchange and the National Stock Exchange.
Stock Index
- It is a sector-wise performance indicator of the stock market.
- It tracks the price shifts of a stock over time.
- For instance, the Standard & Poor’s 500 Index consists of 500 widely held blue-chip stocks chosen because they represent large segments of the American economy.
Various Players in the Stock Market
The most dominant and essential players in the stock markets are,
1. Regulatory bodies: These are the public establishments in charge of developing and implementing policies to supervise the market. It also reviews and approves applications for the issuance of securities in the market.
2. The stock Exchanges: They are private entities where publicly offered securities are listed and traded. They allow investors to route their orders through the stock exchange and bilateral buying and selling mechanisms.
3. Investors: Investors are people who make investments in the securities market. There are different types of investors, like speculators, long-term investors, institutional investors, etc.
4. Brokers:Brokers act as intermediaries between investors and stock exchanges, either advising investors on stocks or executing trades on their behalf. They earn through commissions or brokerage fees and must be licensed by regulatory authorities.
- Full-Service Brokers: These brokers provide research, portfolio management, and advisory services to clients.
- Discount Brokers: They offer lower fees but minimal guidance, catering to self-directed investors.
Binary Brokers: Specializing in binary trading, these binary options brokers enable investors to speculate on asset price movements over a short period. They provide platforms for high-risk, high-reward trading, often with fixed payout structures. - Forex Brokers: These brokers focus on currency trading and may offer leveraged trading opportunities.
5. Issuers: These are public and private entities that conduct public offerings of securities for sale. These offers can occur for fixed-income securities (bonds) or equity securities (shares in the issuing company).
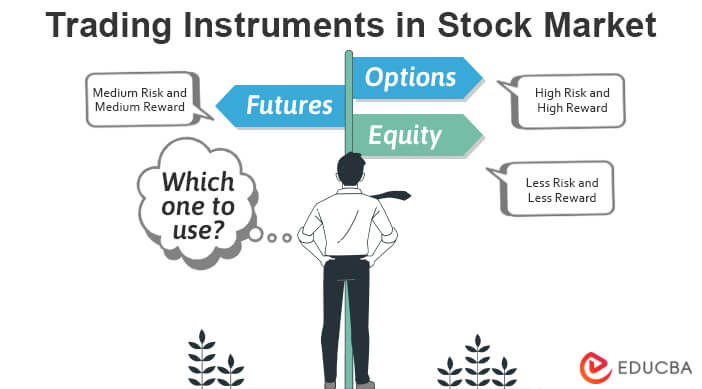
Instruments Traded in the Stock Market
Financial instruments confer ownership rights and issuer obligations under the current legal system. Financial instruments offer varying profitability, risk, and liquidity depending on their characteristics.
Equity
- Equity instruments are generally stocks or shares of a company. These are instruments investors invest the most in.
- The owner has the most equity, whereas shareholders and investors trade for a part of the business on the stock exchange.
- It also offers better liquidity and returns than other instruments.
Mutual Funds
- Mutual funds are instruments where a group of investors mutually pool their funds to make investments.
- It invests in financial products like stocks, bills, bonds, and other funds or non-financial products such as real estate, art, etc.
- Either a company or a trust manages the mutual funds. They also provide numerous tax benefits to taxpayers.
ETFs
- ETFs trade the same way that stocks do. ETFs, like mutual funds, invest in baskets of stocks, bonds, or other assets.
- However, ETFs are advantageous regarding tax efficiency, costs, and transparency about holdings.
- They are versatile, flexible, and typically have low internal expenses.
- They also help in diversifying the investment portfolio.
Debt Instruments
- Debt instruments bind issuers to recurrent payments like coupons in return for access to capital.
- The primary markets issue them before being renegotiated in the secondary market.
- Bonds are debt securities issued by public (government) and private (company) entities to fund their operations.
- The issuer promises to return the principal as well as the interest.
Derivative Instruments
- Derivative instruments are contracts that authorize future trading. Using them, investors can choose a future time and rate to carry out the trade.
- The common types are futures and options; therefore, derivatives are also called Futures & Options stocks.
- The contract reflects data like the volume of the asset, the contract’s length, and other singularities.
How Can You Invest in Stock Market?
As a beginner, investing can be intimidating, but with guidance, anyone can trade. Here are the steps to invest in the stock market.
#1. Assess your Investment Goals
- Knowing the purpose of your investment is necessary. Deciding on a specific goal will be a helpful start.
- Consider what you want to achieve and list your objectives so you can plan your strategy accordingly.
- For instance, you may want to save money for retirement, your children’s college, or a car’s downpayment.
#2. Choose an Investment Platform and Create a Trading Account
- Open an account with a brokerage firm to buy and sell securities through their online platform.
- People typically use free or low-cost discount brokers.
- Full-service brokers are another option, where you get an investment advisor to advise you on your investments.
#3. Research Your Stocks
- Companies publish annual and quarterly financial statements that can be an effective research tool.
- When selecting stocks, you attempt to forecast the company’s future performance. Thus, use those documents to determine if it’s a worthwhile investment.
- Choose stocks (shares, bonds, funds, etc.) based on your investment strategy.
- Also, invest in varieties to diversify your portfolio.
#4. Think About Your Risk Tolerance & Budget
- Stocks move based on rumors and news rather than reported earnings. As a result, stocks in the short term are hazardous. Thus, work out your risk tolerance or the ability to handle a loss.
- Also, decide your time horizon (long-term or short-term) while considering risks.
- Accordingly, calculate your wealth (assets, liabilities, capital) to create a budget for your investments.
#5. Create a Trading Strategy
- To be successful, practice investments that suit your specific investment objectives.
- You now know what you intend to invest in and the purpose. You can now create a plan to meet your investment goals.
- If you prefer short-term trading, standard methods are intraday, swing, and position trading.
- New investors begin with stocks and bonds, as they are straightforward.
#6. Start Trading
- After researching and determining which securities to purchase, start trading.
- Depending on your trade choice (buy/sell), open a trade position and offer a bid/ask price.
- Always start low and increase your investment amount gradually.
- You can also consider demo trading, where you trade in the real stock market for imaginative money before investing the remaining funds.
#7. Keep Track of Your Investments
- After the initial investments, keep track of the performance.
- Be aware of issues and fluctuations in the market. Base the type of monitoring on your investment strategy.
- For long-term goals, review the portfolio every six months. Check your short- or medium-term portfolio at least once a month.
- Day-to-day or very short-term investments may require daily or even hourly monitoring.
How Should You Choose Stocks to Buy?
The stock market is a complex and confusing marketplace. Therefore, picking stocks to invest in can be difficult. These are some tips for choosing stocks.
a) Have an End Objective
- An investment is a calculated risk. Thus when choosing stocks, you must know your end goal.
- Invest for the long haul and not for quick money-making.
- Think about the time and effort you can put in, along with the types of investments that interest you, to make intelligent investing decisions.
b) Don’t be Afraid to be Different
- Besides understanding how to choose stocks, knowing what not to do is also important.
- Do your research, and don’t buy stocks just because they’re famous or your friend told you.
- Look for stocks that are undervalued and can assure future success.
- Try buying stocks with a low P/E ratio and an upward-trending price chart.
c) Set your Risk Manually
- Attain portfolio diversification by investing in different stocks.
- When considering risk, consider the time you are willing to hold onto the stock.
- Start with low-risk stocks like index funds and work up to higher-risk stocks.
d) Know your Investments
- Invest in what you know and understand.
- It will also help you avoid panicking when something goes wrong with the company or an important product.
- More knowledge about your investments will lead to fewer mistakes.
e) Understanding Financial Ratios
- Financial ratios allow you to compare the company’s performance over time and against industry peers.
- These are numbers that determine the company’s financial aspects.
- Some prominent ratios include P/E, ROE, EPS, ICR, etc.
Financial Ratios to Consider While Investing in Stocks
Financial ratios are a company’s accounting indicators. They allow us to compare the company’s situation and development over time. Here are a few critical ratios for stock investments.
- P/E Ratio: This is among the most popular and widely used investment indicators. This ratio determines the value of a company. It helps discover if the company is under or overvalued.
Formula: Price-earnings ratio = Share Price / Earnings per share
- Quick Ratio: The acid test ratio is the ratio of a company’s quick assets to its total current liabilities. It tests a company’s ability to pay its obligations. A proportion of at least 1:1 would satisfy creditors. In contrast, a low ratio could indicate that the company will struggle to pay its bills.
Formula: Quick ratio = Current Assets – Inventories / Current Liabilities
- ROE Ratio: Return on Equity is a profitability ratio that assesses how good a company’s equity is. It indicates the income a company is generating for every dollar of equity. A higher percentage is considerably better.
Formula: Return on Equity ratio = Net income / Shareholder’s equity
- Price to Book Ratio: The P/B ratio compares a company’s book value to its current market price. It indicates if an investor is overpaying for the shares. It usually tells whether a stock is overpriced or underpriced.
Formula: P/B Ratio = Share Price / Book Value per Share
- Dividend Payout Ratio: It assists investors in determining investment-worthy companies. The ratio indicates a company’s potential for future growth. Thus, a consistently high dividend payout rate may not be a good sign for investors looking for high-growth companies.
Formula: Dividend Payout = Dividends / Net Income
- EBIT: Earnings Before Interest and Taxes present the net income before deducting income tax and interest expenses. It is also known as operating income. It assesses the performance of a company’s core operations without accounting for capital structure and tax expenses.
Formula: EBIT = Revenue – COGS – Operating Expenses
EBIT = Net Profit Earned + Interest & Tax Expenses.
- Debt to Equity Ratio: This ratio measures a company’s financial leverage. It helps analysts and investors understand a company’s financial structure and whether it is a good investment. Considering other factors to be equal, the higher the debt-to-equity ratio, the riskier the company.
Formula: Debt to Equity Ratio = Total Liabilities / Total Equity
- Price/Earnings to Growth Ratio: This ratio shows how expensive or cheap a company’s stock is. A lower rate indicates the company is currently undervalued based on its earnings performance. In contrast, a higher rate suggests overvaluation.
Formula: PEG Ratio = P/E ratio / EPS Growth Rate
- Dividend Yield Ratio: It measures the number of dividends attributed to shareholders relative to the market value per share. The dividend yield is an estimate of return that only includes dividends from a stock investment. This ratio communicates the value of the return received by investors. It rises when the stock price falls and falls when the stock price rises.
Formula: Dividend Yield Ratio = Dividend Per Share / Share Price
- Earnings Per Share: EPS is the most common ratio for investors. It determines the net income earned for each outstanding share. This value can further calculate various other company financial metrics.
Formula: Eps Ratio = Net Earnings / Weighted Average Shares Outstanding
How are Stock Markets Regulated?
- The stock markets of every country have their regulatory bodies. For instance, SEBI is Indian, CSA is for Canada, SEC is for the U.S., and so on.
- These regulatory bodies protect investors from insider trading, fraud, and other potential misconduct. While over-regulation could lead to its problems, under-regulation can result in abuse by corporations or managers.
- The regulators have three primary responsibilities: enforcing federal securities laws, monitoring market activity, and providing oversight.
- Companies need to register with the regulations. They also have to submit quarterly and annual financial reports.
- The regulatory boards then review these documents to detect any violations. If they find any violations, they set up an investigation. If guilty, the individual or company may have to pay the penalty and be unable to trade in the securities market.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Q1. What is the stock market? What are the types of stocks?
Answer: The stock market is a platform with various stock exchanges, which enables traders and investors to buy and sell securities and shares of public companies. There are multiple types of stocks for investors’ plans. The most common are the preferred and common stocks. The other types of stocks are growth, hybrid, penny, defensive, etc.
Q2. How to invest in the stock market? What app can I use?
Answer: The first thing to do to invest in the stock market is to select a reputable and competitive broker. Create your trading account and add capital to it. Remember to choose a stock after thorough research and analysis. Then you can invest in stocks through your account. Angel one, Zerodha, and Wealthfront are some apps you can use.
Q3. When does the stock market open? Does it work on weekends?
Answer: Every stock exchange has different trading hours. The London stock exchange opens at 8:00 a.m., whereas the Australian securities exchange does not open till 10:00 a.m. However, the standard working hours are 9:00 a.m. to 4:00 p.m. Additionally, all stock markets are closed on weekends.
Q4. Is it suitable for beginners? What are some courses on the stock market or investment banking?
Yes, it is excellent for beginners to learn and trade in the stock market. You can learn valuable courses from the NSE India, the Colombian Stock Exchange, and many more. Opting for a whole Investment Banking Bundle will prove more beneficial.
Q5. Should I invest in the stock market? Where to invest?
Investing in the stock market is beneficial as there is a potential for high returns. However, the value of your investment could fall dramatically. To invest in the stock market, you must make wise decisions. Perform research and choose financially sound companies. You can use trading platforms like 5paisa, Groww, etc., to invest in the stock market.
Recommended Articles
This was a guide to What is Stock Market. To learn more, please read the following articles: