Overview Structured Finance –
Structured finance is a composite financial instrument offered to borrowers with unique and sophisticated needs. Structured finance is referring to more complicated financing than traditional loan products. More specifically, it is also used to describe financing transactions which help transfer risk as applied to securitizations of various assets, for example, Auto Loan.
Following are structured finance products-
- Asset-backed securities (ABS)
- Mortgage-backed securities (MBS)
- Collateralized mortgage obligations (CMOS)
- Collateralized debt obligations (CDOs)
- Credit derivatives
Terminology in structured Finance
Securitization –
It is a process in which non-tradable assets are packaged and converted into financial security and then finally sold. It is a process in which the entity securitizing its assets is not borrowing but selling a stream of cash flows that were otherwise to accrue to it. It’s a device of structured products in which an entity seeks to pool together its interest in identifiable cash flows over time, transfer same to the investor either with or without the support of further collateral and there by achieving the purpose of financing. Securitization is the process of creating new securities by pooling together various cash-flow producing financial assets.
Securitization Process-
- The originator either has or creates the underlying assets, i.e. transaction receivables to be securitized.
- Selection of receivables to be assigned
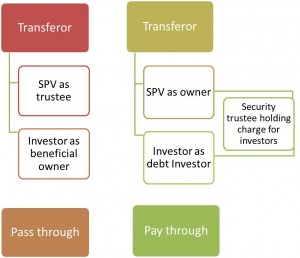
- Formation of special purpose vehicle(SPV)
- special purpose vehicle(SPV) acquires the receivables under a discounted value
- The servicer for the transaction is appointed (normally originator)
- Servicer collects the receivables (usually escrow mechanism) and pays off the collection to special purpose vehicle(SPV)
- The special purpose vehicle(SPV) either pass the collection to the investor (or reinvest the same to pay off)
- In case of default, the servicer takes action against debtors as a special purpose vehicle(SPV)s agent
- When an only a small amount of o/s receivables are left to be collected, the originator usually cleans up the transaction by buying back the o/s receivables
- At the end of the transaction, the originator profit, if retained and subject to any losses to the extent agreed by the originator in the transaction is paid off
Concept of SPV-
Use of Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs)-
- Generic use of SPVs – to isolate identifiable assets/risks into a stand-alone, self-sustained identifiable which is no more than such assets/ risks.
- Special Purpose Vehicles are used in securitization transactions as devices of hiving off assets and converting assets into securities.
- A Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) is no more and no less than incorporated name for specific assets.
Asset-backed security-
Financial security backed by a loan, lease or receivables against assets. These are bonds or notes based on pools of assets, or collateralized by the cash flows from a specified pool of underlying assets. Asset-backed securities are also called ABS, Generally these assets consist of receivables other than mortgage loans, such as credit card receivables, auto loans, it differs from most other kinds of bonds in that their creditworthiness (which is at the AAA level) derives from sources other than the paying ability of the originator of the underlying assets. In simple words, we can say that ABS is a security backed by the pool of assets.
Mortgage-backed securities (MBS)-
Mortgage-backed securities (MBS) are asset-backed securities are backed by the principal and interest payments of mortgage loans. They represent an interest in a pool of mortgage loans. It is a type of asset-backed security that is secured by a pool of mortgage. These securities are grouped in one of the top two ratings as determined by credit rating agencies, like S & P, and usually, pay periodic payments that are similar to interest payments.
Collateralized mortgage obligations (CMOS)-
These are securitizations of mortgage-backed securities. It is a type of mortgage-backed security that creates separate pools of pass-through rates for different classes of bondholders with varying maturities, called tranches or slices. They are created from a pool of mortgage pass-through securities. Collateralized mortgage obligations (CMOs) investors receive interest and/or principal payments from the mortgage securities in a predetermined manner.
Credit Derivative-
Credit derivatives are derivative instruments that seek to trade in credit risks. The main purpose of credit derivatives is to hedge. Counterparty is trying to transfer credit risk, called a protection buyer, and the counterparty is trying to acquire credit risk, called a protection seller. When any credit event occurs then the protection seller compensates the protection buyer.
- Credit events maybe
- Bankruptcy
- Default (failure to pay)
- Capital restructuring
- Merger and acquisition activity
Typical Originators of securitization-
- Mortgage financiers
- Banks
- Finance companies
- Credit card companies
- Hoteliers
- Public utilities
- Intellectual property holders
- Insurance companies
- Aviation companies
- Governments