Definition: Virtualization
Virtualization is the technology to generate virtual instances of computer resources for multiple uses of the same physical resource. Several virtualization technologies can virtualize the server, storage, networks, and operating systems. The technology is known for ease of setup and environment setup cost optimization with higher processing efficiency.
The virtualization environment shared the actual resources component such as Memory(RAM), disk space, and network as a separate resource group. Thus, it helps organizations to scale the computation resources. Virtual machines (VM) are the popular hardware virtualization uses managed through the hypervisor.
How does it Work?
This is a single physical machine with multiple virtual machines. Large companies with dozens and even hundreds of servers use server virtualization to increase their operating effectiveness and consolidate the number of machines running. It can help businesses by allowing them to maintain fewer devices, use them better, and ensure more reliable backup and recovery. Once a virtual server is configured, you can configure the new virtual servers using the same configuration, which only takes several minutes.
Benefits
Given below are the benefits mentioned:
- It saves space as well as operating costs.
- Easy management of the data centers.
- It can increase the Productivity of IT.
- It helps to continue working if the system crashes or any sudden failures.
- Applications and resources are provided more quickly while using virtualization.
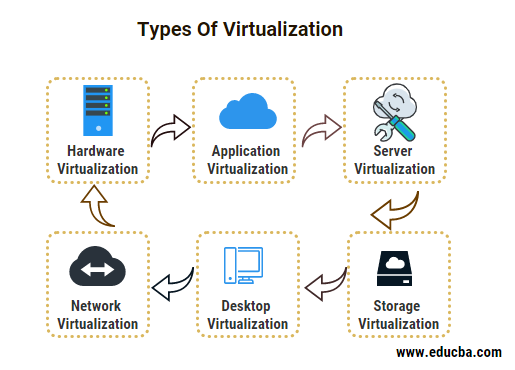
Types of Virtualization
Given below are the types mentioned:
- Hardware Virtualization
- Application Virtualization
- Server Virtualization
- Network Virtualization
- Desktop Virtualization
- Storage Virtualization
1. Hardware
A virtual machine manager (VM), called a hypervisor, makes hardware virtualization possible. The hypervisor creates and consolidates virtual versions of computers and operating systems into one large physical server, making it possible to use all hardware resources more efficiently. Users can have multiple operating systems on the same machine simultaneously.
2. Application
In Application virtual, applications are virtualized on the server. After that, the Application is sent from the server to the end-user’s devices. Instead of logging into their work computers, users can access the Application directly from their device with a proper internet connection.
3. Server
The virtualization of servers is masking server resources from server users, including the number and identity of physical servers, processors, and operating systems.
There are some popular server virtualization approaches which are as follows:
- Virtual machine model: Host/Guest paradigms are based on a virtual machine. This approach enables the guest operating system to operate without change.
- Paravirtual machine model: Host/Guest paradigms are based on virtual machines and are used in virtual machine monitors.
- Operating system layer: The operating system layer is not based on paradigms; this OS layer model runs on a single OS kernel.
4. Network
This (NV) means a hardware platform is simulated. For example, a software server, storage device, or network resource. It provides a summary for networking and services through hardware into a logical, virtual network connected to a physical network on a hypervisor and operates independently from the network. It can provide a virtual network that is truly independent of other network resources in a virtual environment.
Different types of network virtualization exist, such as external and internal NV. External NV is a combination of different networks located in different places. In Internal NV, you divide the network into a single system.
5. Desktop
We often call Desktop client virtualization. This desktop technique separates the physical computer from the computer desktop environment. You can interact the same way you use a physical desktop on a virtual desktop. It reduces the cost of software licenses and updates. Furthermore, you can easily manage patching and system maintenance since all the virtual desktops are hosted in the same place. Another advantage of desktop virtualization is to log in from any location to access your desktop remotely. It has been used in server computing models.
6. Storage
Storage is essential and valuable when there are sudden system breakdowns. You can achieve it by assembling the physical hard drives into one cluster. In the time of crashing or unavailability of the hardware or software, the user can recover data from this. You can store and move copies of data to another location. You can implement it using software applications or simultaneously utilizing software and hardware devices.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Virtualization
Given below are the advantages and disadvantages mentioned:
Advantages:
- You don’t require actual hardware components for installation.
- You can access it from a third party or purchase the licenses.
- The most frequent providers of virtualization automatically update their helpful hardware and software. A third-party provider installs them instead of sending individuals for local updates.
- Digital entrepreneurship was practically impossible for an average person before virtualization took place on a large scale.
- Energy consumption decreases because virtualization reduces power consumption on physical servers.
- When you can install dozens of servers on the same computer, the cost of additional servers is almost nonexistent.
Disadvantages:
- Not every Application or server will work in a virtualization environment.
- You will need to invest in training existing network administrators who do not have the capabilities to manage a virtual network.
- In a virtualized system, when something goes wrong, it requires complex troubleshooting.
- The difficulty lies in the nearly impossible estimation of the extra resources needed in advance.
Conclusion
In this article, we covered the meaning and how it works. Also, there is a descriptive guide on types and their advantages and disadvantages. Initially, businesses may find any type of virtualization complex and confusing, but with time and practice, it becomes easier, saves time and costs, and proves effective for any business.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to What is Virtualization? Here we discuss the basic concept, benefits, advantages, disadvantages, and types of virtualization. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –