Updated July 28, 2023
Introduction to VLAN Network
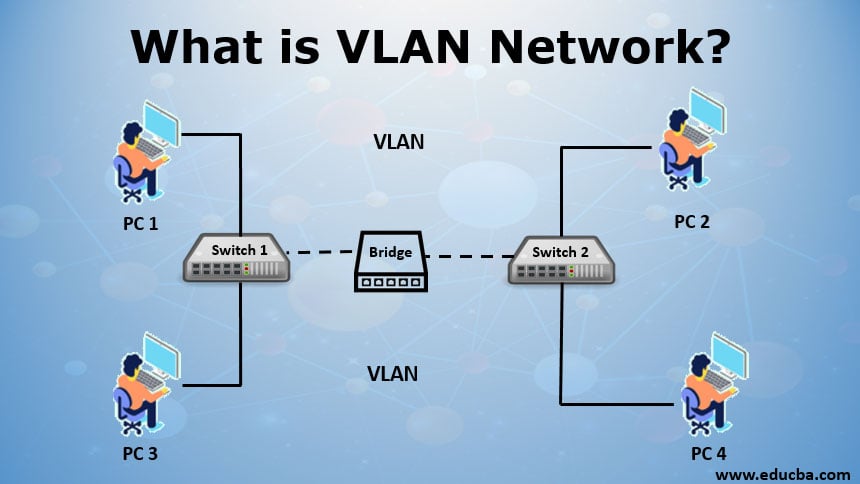
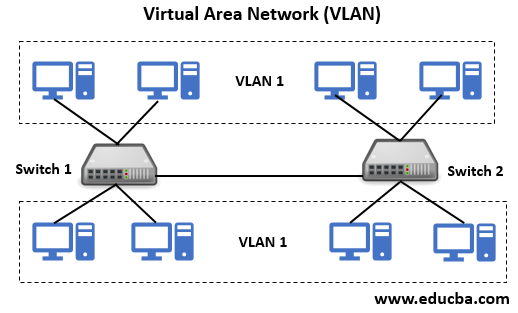
VLAN is a logical system grouping in the same area of the broadcast. Usually, VLANs are configured on switches by putting interfaces in one and many interfaces on another broadcast domain. VLANs can be distributed over several switches, each of which is regarded as its own broadcast or subnet domain. This means that only ports within one VLAN are swapped between frames transmitted to the network. A VLAN behaves like a physical LAN, enabling the host to link into the same broadcast area, even if it is not connected to the same switch.
Types of VLAN Network
Given below are different types of VLAN Network:
- Using their network traffic carried by each type gives a particular name.
- Their own type derives names.
- It can be derived using their specific functionality as well.
Few Common Types of VLAN are as follows:
1. Default VLAN
When a switch gets booted up for the first time, all the ports of the switch will turn to default’s VLAN member. Having all the ports in default VLAN, it is combined to have its parts to the same domain for broadcasting the network. Using this, any device can connect to different switch ports for communication between any devices on any ports.
Cisco switches use Default VLAN, and its name is VLAN1. VLAN1 adheres to every feature of default VLAN, but except one feature. VLAN1 does not allow to rename its types or port, and it does not allow to delete. Its role is to control the traffic over Layer 2 of the network.
2. Data VLAN
Data VLAN is termed User VLAN because it helps to carry the traffic generated by the user. The common practice of the VLAN is to separate the voice and management traffic from the data traffic. The importance of separating the user data from switch management control data and voice traffic is highlighted and uses a special term to identify VLANs among other VLANs is => which carries only user data is a “data VLAN”.
3. Voice VLAN
Voice VLAN has the configuration to carry the voice traffic over the network. Among all the VLANs, Voice VLAN has a high transmission priority over other network traffic types. Phone calls complete the process of communication over the network. So more calls are made over the network than other forms of messages. The legitimacy and assurance are achieved only through real voice, rather than communication through emails or text messages.
The voice calls should be routed with 150-180 milliseconds delay (i.e. minimal delay) over the network. This type of design in congested areas will give good voice quality. Network administrators design the network that supports VoIP (voice over IP) with assured bandwidth to ensure better voice quality.
For E.g. if an organization uses VoIP, it’ll have a separate voice VLAN and allows preserving bandwidth for applications and ensure VoIP quality.
4. Native VLAN
Native VLAN will experience traffic called untagged traffic placed on a trunk port. This set up provides support that native VLAN can take the traffic, and it can identify the traffic that comes from any part of the trunk link. The 802.1Q trunk port gives this support. The trunk port makes it possible for native VLAN to support any legacy devices that don’t tag their traffic to a wireless access point or network-attached devices.
5. Management VLAN
All the capabilities of the switch are given access for managing in VLAN is said as Management VLAN. This access is configured in VLAN to manage and keep under control. The set up provides the best practice that VLAN is used for managing traffic tasks like monitoring, system logging, SNMP, etc. This configuration as a management VLAN is assigned to a specific address and allows subnetting too.
Another advantage of this VLAN is, any switch VLAN is configured as a management VLAN, and it serves its own tasks. if VLAN doesn’t have management configuration or it is called & featured as VLAN with unique. The security benefits are also ensured during the high user traffic, with the availability of bandwidth for management.
Sometimes, network administrators assign VLAN1 as management VLAN. We can connect with unauthorized access to a switch and identify as an alternative or shortcut way to connect a switch.
How does VLAN Work?
Each VLAN is configured to an Ethernet switch that acts as a physical bridge, and it can perform filtering, forwarding, learning and loop elimination mechanisms, etc. The hosts can be grouped together by the network administrators though the hosts are not connected on the same network switch.
For example, In an organization, the users are connected to the VLAN, and it helps to separate the traffic within the connected network. It helps users by segregating the low traffic based on priority to directly affect the network functionalities.
Many hosting services use VLANs, and it helps to separate the customers from private zones from each other and allows each customer servers to group together to a single network segment by identifying and connecting to locality being anywhere in their data center. A switch can define one or more virtual bridges. So each bridge in the switch refers to the new broadcast domain (i.e. VLAN).
Either within the switch or between two switches, one VLAN cannot allow the traffic to another VLAN. To overcome this problem, routers or Layer 3 switches (i.e. Gigabit Ethernet switch & 10GbE switch) is used to interconnect the two different VLANs.
VLAN can be defined, and working differs on different types and methodologies. VLAN is defined with two other types:
- Port-based VLANs (untagged): In this type, a single physical switch is used to divide into multiple logical switches.
- Tagged VLAN: In this type, we can use a single port switch to connect multiple VLANs. Here, the VLAN identifier identifies the frame to be connected with Ethernet frames in the port. If both switches understand tagged VLANs’ operation, a reciprocal connection is accomplished using one single cable connection from the “trunk port.”
VLAN membership can be assigned to a device by any two methods Static and Dynamic membership.
There are other methodologies used to accomplish on different layers of the OSI model:
- Port-based creation method (corresponds to Physical layer)
- MAC-based creation method (corresponds Data-link layer)
- Layer-3 based method (corresponds to Network layer)
- Rules-based method (Enable to access frames and selectively uses fields or bits).
Advantages of VLAN Network
- VLANs have a number of advantages over traditional LANs.
- Removed physical barriers to connect between networks.
- Simplified design: Even the physical machine moves from one to another location, VLAN stays the same without any hardware reconfiguration.
- Improved Performance: Efficiency is improved due to reducing size in the broadcast domain.
- Security: VLAN restricts access with authentication setup, and constraints can be introduced in trunk protocol to identify the user connection with a specific VLAN.
- Reduce costs due to the segmentation of VLAN through routers.
Conclusion
Compared to other network commuters, VLANs are an integral part of every enterprise network by giving flexibility and security. The main problem was to troubleshoot the problems on the network. VLAN handled easier fault management by segmentation and isolation of networks. So the issues can be narrowed down by identifying the subnet of users and can be resolved quickly.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to What is VLAN Network? Here we discuss how it works, different types of VLAN with their advantages. you may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –

