Updated March 17, 2023
Difference Between Wi-Fi and Ethernet
Wi-Fi vs Ethernet is the comparative technologies for internet access. The evolution of internet technologies and wireless access to the internet, gaining a high demand for both business and personal use. Wi-Fi is the technology that uses radio waves to connect mobile and access devices through the internet. Whereas Ethernet is based upon LAN and physical wired connection for internet communication. Wi-Fi is easy to set up and configure, whereas Ethernet is a bit difficult to need experienced professionals to set up. Wi-Fi provides a slower transfer speed compared to Ethernet. For Wi-Fi, data encryption is recommended, whereas Ethernet data security is higher compared to Wi-Fi.
What is Wi-Fi?
Wi-Fi is a network technology that enables mobile devices to connect to the Internet wirelessly or to promote wireless communication. Wireless LANs have exponentially evolved from high-priced network solutions to mainstream innovation in just a few years. The elimination of the networking port from the equation and separating the device connection from the direct physical position at the end of the cord has certainly made wireless LANs simple and functional. The best thing about wireless service is a mobility-without cable; no cabling means easy movement and expansion. A free wireless network was developed with the concept of Wi-Fi technology. Mobility is the clearest advantage of wireless networking.
What is Ethernet?
Ethernet is the most widely used technology in wired local communications networks and a generic communication protocol. First released in 1980 by the DIX (Xerox, Intel, DEC) group, the original 10 Mbps Ethernet specification was called a DIX Ethernet standard. As a result, the coaxial varieties of Ethernet are ending up being standardized twice-first by the DIX group and then by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. The new program was led by the Institute of Electrical And Electronics Engineer. The two parties had different objectives, and the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers made some changes to the original DIX standard. For the OSI physical layer of TCP / IP, the Ethernet defines wire and signaling standards.
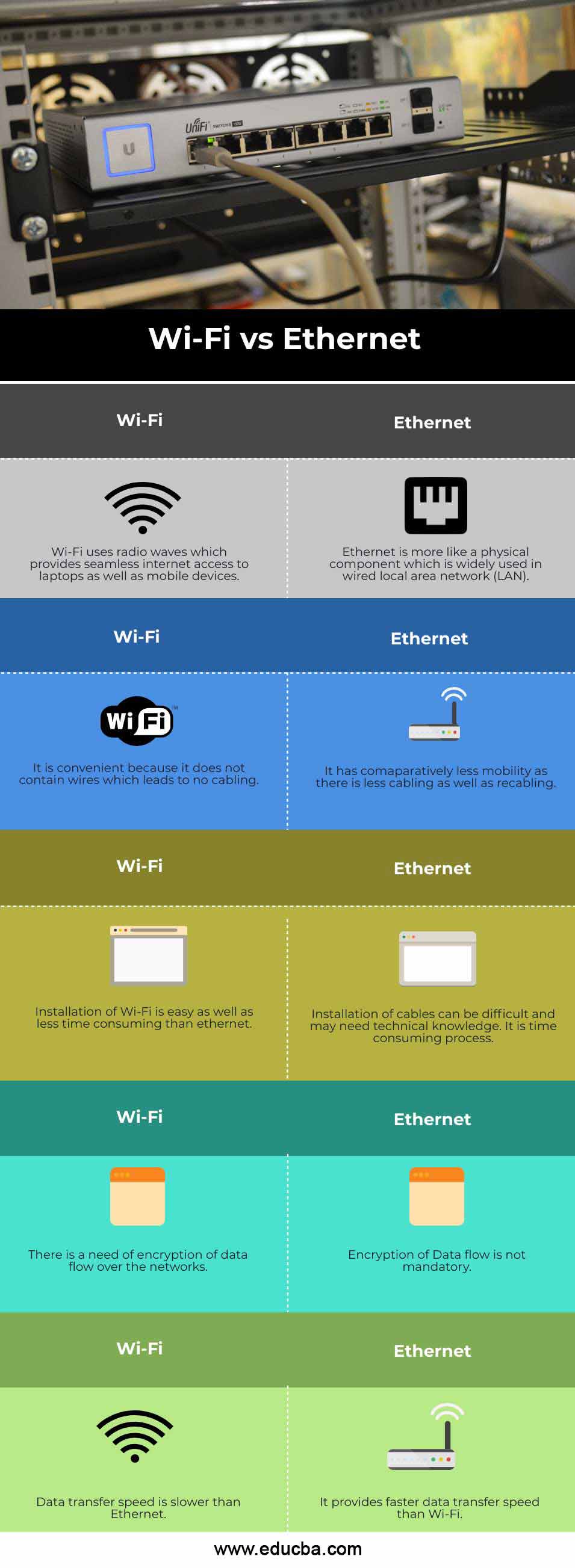
Head to Head Comparison between Wi-Fi and Ethernet (Infographics)
Below is the top 5 Comparison between Wi-Fi vs Ethernet:
Key Differences between Wi-Fi and Ethernet
Let’s discuss the top comparison between Wi-Fi vs Ethernet:
- Wi-Fi is a networking system that provides mobile devices with wireless internet connectivity and wireless communication. It is a technology that uses radio waves to link to devices based on the IEEE 802.11 high-speed Internet connection.
- On the other hand, Ethernet is a generic networking protocol and the most common technology for wired LANs. It refers simply to the physical cable or internet cable that moves that data. one of the main differences between both and Wi-Fi over Ethernet is mobility.
- Wi-Fi is the most popular type of internet access today, which provides users with constant access to data that can result in large productivity improvements.
- It is perfect for people who are always on the go and want to simultaneously access the Internet from several locations. Wireless Internet means no cables and no cables, and no ports. Ethernet is cables that mean lots of cables so that no mobility is involved.
- Wireless networking has the most apparent advantage of flexibility. Wireless link does not include cables that do not require recovery. This is also the easiest and most comfortable since no cables need to be mounted.
- Wireless networks allow you to create small group networks quickly for a quick official meeting, and Wi-Fi makes it easy to switch between rooms and cubicles. An Ethernet connection provides the same speed. If you download large files, you will notice this quick and stable speed.
- Ethernet connections can also be used for HD video streaming. Because of many environmental factors, Wi-Fi suffers from signal interference. And the atmosphere can cause problems, and Wi-Fi often produces poor efficiency. As you move from one place to another in your room, you will notice intermittent signals.
- This can be reduced by putting your router in your room or office in an optimal position, but it doesn’t remain easy to achieve the same reliable Ethernet connections efficiency.
Comparison Table of Wi-Fi vs Ethernet
The table below summarizes the comparisons between Wi-Fi vs Ethernet:
|
Wi-Fi |
Ethernet |
| Wi-Fi uses radio waves which provide seamless internet access to laptops as well as mobile devices. | Ethernet is more like a physical component which is widely used in wired local area network (LAN) |
| It is convenient because it does not contain wires which leads to no cabling. | It has comparatively less mobility as there is less cabling as well as recabling. |
| Installation of Wi-Fi is easy as well as less time consuming than ethernet. | Installation of cables can be difficult and may need technical knowledge. It is a time-consuming process. |
| There is a need for encryption of data flow over the networks. | Encryption of Data flow is not mandatory. |
| Data transfer speed is slower than Ethernet. | It provides faster data transfer speed than Wi-Fi. |
Conclusion
In this article, we have seen the key differences between Wi-Fi and Ethernet. I hope this article will help you to choose a better option for your internet connectivity based on your needs.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the top difference between Wi-Fi vs Ethernet. Here we also discuss the Wi-Fi vs Ethernet key differences with infographics and a comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –