Updated April 4, 2023
Difference Between Wifi vs Hotspot
In this topic, we are going to learn about WiFi vs Hotspot. Wi-Fi is a LAN (Local Area Networks) cellular networking technology. For wireless networking, Wi-Fi uses electromagnetic waves under the 2.4 GHz radio frequency bands. To build a hotspot, WLAN is created by using the wireless device. Without broadband internet, there will be no hotspot. In nature, wifi is safer and more versatile. You can connect game consoles, laptops, printers, etc.
The hotspot is equipped for wireless Internet connectivity. The hotspot delivers wireless Internet connectivity through wireless internet access. A hotspot is generated with an access point system, but a hotspot and an access point will mean the same when used normally. A portal or router connecting to the Internet typically has an access point. The hotspot is less safe than private Wi-Fi since it is usually used in public places.
Head to Head Comparison Between WiFi vs Hotspot (Infographics)
Below are the top differences between WiFi and Hotspot
Key Differences between Wifi vs Hotspot
Following are the key differences between Wifi vs Hotspot.
- Both the Wi-Fi internet connectivity and the Hotspot are common concepts that are used in combination with the cellular Internet connection. Wi-Fi is a wireless networking technology that helps you to establish a Wi-Fi-based Wi-Fi network that provides easy access to the Internet. On the other hand, a Hotspot is a wireless access point that provides wireless internet access through local wireless networks (WLAN).
- Wi-Fi is an IEEE 802.11-based wireless network protocol that uses radio waves to provide networking access to mobile devices. Wi-Fi is a satellite link, as is the case for network cables. It is much like a local wireless network used to link computers without cables together. Hotspot refers to wireless points that commonly use Wi-Fi for Internet communications from a physical venue.
- Wi-Fi is like a closed access network where the network provider can select who is willing or unwilling to access its Wi-Fi network in complete power. The owner may change either the Wi-Fi or password or even restrict the number of customers connecting to the network by restricting access to the network. You can also turn off the Wi-Fi modem and close the network connection. Hotspot venues are primarily airports, restaurants, coffee shops, and roads that are easily open to service providers.
- The traditional 2.4 GHz radio frequency band is used for the connection of Wi-Fi routers for devices typically of a restricted range. The range is constrained by the antennas or the position in or around them. Typical Wi-Fi indoors can be built up to 32 meters, and outdoors can also be spread in the stations, up to several kilometers. With the support of the Wi-Fi range extensor, which is yet another computer with an IP address, Wi-Fi signals may also be improved. In the range of 33 ft, hotspot signals can be accessed.
- The vulnerability of wireless networks is greater, especially public Wi-Fi networks, to hacking because you are not the sole network linked. Generally speaking, the infringement is extremely improbable in terms of protection for anyone linked to the network that is WPA2-protected. There are dangers, however, as relaxed as public Wi-Fi. Hotspots are actual places, and almost everyone can reach the internet, making it a perfect venue for cyber attacks. Using a VPN might be a perfect way to keep a hotspot secure.
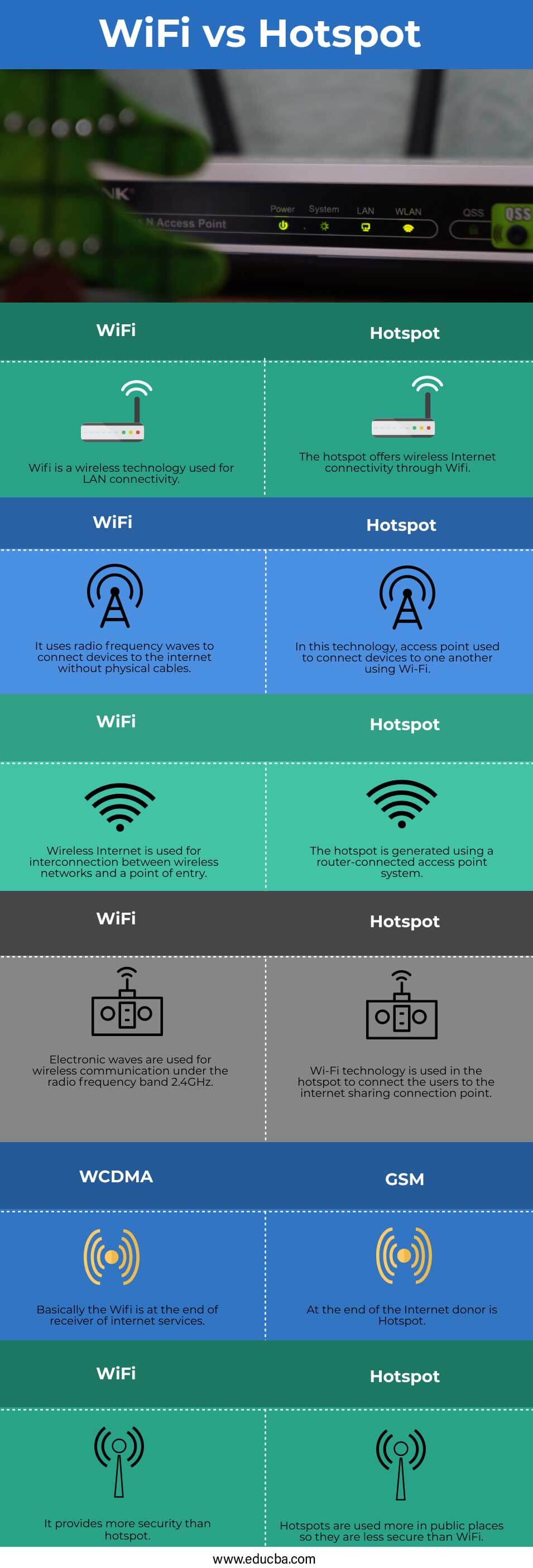
WiFi vs Hotspot Comparison Table
Let’s see some more differences between WiFi vs Hotspot through a comparison table for clear understanding:
| Sr no | Wifi | Hotspot |
| 1 | WiFi is a wireless technology used for LAN connectivity. | The hotspot offers wireless Internet connectivity through Wi-Fi. |
| 2 | It uses radiofrequency waves to connect devices to the internet without physical cables | In this technology, the access point used to connect devices using Wi-Fi |
| 3 | Wireless Internet is used for interconnection between wireless networks and a point of entry. | The hotspot is generated using a router-connected access point system. |
| 4 | Electronic waves are used for wireless communication under the radio frequency band 2.4GHz. | Wi-Fi technology is used in the hotspot to connect the users to the internet sharing connection point |
| 5 | Basically, the Wifi is at the end of the receiver of internet services. | At the end of the Internet, the donor is Hotspot. |
| 6 | It provides more security than a hotspot | Hotspots are used more in public places, so they are less secure than WiFi |
Conclusion
WLAN is a wireless networking system that allows users to link on a local area network but does not require physical cables. Wireless Internet uses radiofrequency waves instead of using network wires to link to the internet to make Wi-Fi connectivity between users within a specific region simpler. This is an overall term used to designate a collection of networking protocols to provide high-quality internet connectivity based on IEEE 802.11 specifications. So In this article, we have seen key differences between WiFi and hotspot. We hope you will find this article helpful.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to WiFi vs Hotspot. Here we discuss the WiFi vs Hotspot key differences with infographics and a comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –