Updated March 2, 2023
Introduction to Windows Server Interview Questions And Answers
So you have finally found your dream job in Windows Server but are wondering how to crack the Windows Server Interview and what could be the probable Windows Server Interview Questions. Every interview is different and the scope of a job is different too. Keeping this in mind we have designed the most common 2023 Windows Server Interview Questions and answers to help you get success in your interview.
Below is the top 2023 Windows Server Interview Questions that are asked frequently in an interview. These top interview questions are divided into two parts are as follows:
- Part 1 – Windows Server Interview Questions (Basic)
- Part 2 – Windows Server Interview Questions (Advanced)
Part 1 – Windows Server Interview Questions (Basic)
This first part covers basic Windows Server Interview Questions and answers
1. What is an Active Directory?
Answer:
Active Directory (AD) is a directory service which is used in a directory to store objects like user profiles, network information, computers. It helps to manage the network effectively with the help of Domain Controllers which are present at different locations with the Active Directory database. Some of the functions include central administration with multiple geographical locations, authentication of users and computers in a windows domain, replicating Active Directory from any Domain Controller which in turn will be replicated to all other Domain Controller’s.
2. What are some of the roles of FSMO (flexible single master operations)?
Answer:
- Schema Master is a forest-wide role and is available only on each forest
- Domain Naming Master, like Schema Mater this too is a forest-wide role
- Infrastructure Master
- RID Master
- PDC
Let us move to the next Windows Server Interview Questions
3. Tell me about Active Directory Database And List The Active Directory Database Files?
Answer:
The Active Directory database files as follows:
- DIT
- Log
- Che
- log and Res2.log
All the Active Directory changes are not written directly to the NTDS.DIT database file. They are first written to EDB.Log and thereon from the log file to the database.
EDB.Che is used to tracking the updates to the database it acts as an update log file to check what operations are performed to the database.
- NTDS.DIT: This is the Active Directory database and contains all the AD objects. The default location is %system root%nrdsnrds.dit, this database is based upon the Jet database.
- EDB.Log: This file is to track the transactions on the database, when EDB.Log is full it gets renamed to EDB Num.log where a num is a number starting from 1 like EDB1.log
- EDB.Che: This file is used to check for the data that is not yet written to a database. This file has the starting point to the data can be recovered during failures.
- Res1.log and Res2.log: Res stands for reserved transaction file which provides the transaction log file enough time to shut down if the disk runs out of space.
4. What is the use of Active Directory Partitions? And How to Find the Active Directory Partitions and there Location?
Answer:
The different type’s of active directory partitions are as below:
- Schema Partition–This partition stores all the details of the objects and their attributes, it also replicates to other domain controllers which are present in the Forest
- Configuration Partition– This partition stores all the information about the Active Directory. The information includes Site, site-link, subnet etc. this partition also replicates to all domain controllers which are present in the Forest
- Domain Partitions– This partition stores the information of the domain which includes user, computer, group, printer etc. this partition also replicates to all domain controllers which are present in the domain.
- Application Partition– This partition stores the applications information in Active Directory.Exampels– ForestDNSZones and DomainDNSZones
5. What are GPOs (Group Policy Objects)?
Answer:
This is the frequently asked Windows Server Interview Questions. The settings that control the working environment of user accounts and computer accounts are known as Group Policy Object (GPO). This help is defining the security options, software installation, registry-based policies and maintenance options, script options and folder redirection options
There are two types of Group Policy Objects:
- Nonlocal Group Policy objects: These are available only in an Active Directory environment and are stored on a domain controller
- Local Group Policy Objects: These are stored on local computers (individual computers)
Part 2 – Windows Server Interview Questions (Advanced)
Let us now have a look at the advanced Windows Server Interview Questions.
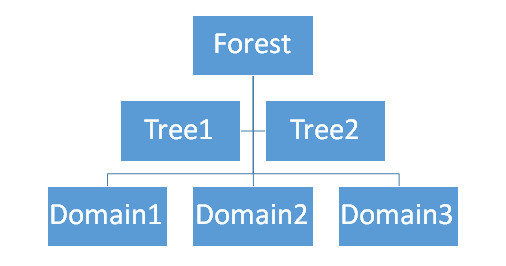
6. What do Forests, Trees, and Domains mean?
Answer:
The logical divisions of an Active Directory network are known as forests, trees, and domains.
A logical group of network objects for example computers, users, devices etc which share the same active directory database is known as a domain.
The collection of one or more domains is known as a tree. This may also include a contiguous namespace linked in a transitive trust hierarchy.
The collection of domains is known as the forest which shares a common global catalog, logical structure, directory configuration and directory schema. It also defines the security boundaries for users, groups, and computers.
7. Non-authoritative Restore of Active Directory?
Answer:
During non-authoritative restore, the domain controller is set back to its initial state (the state at the time of backup was taken). Once it’s done it allows overwriting its initial state with the changes that were done after the initial backup was taken.
Now for updating the Active Directory database, queries are fetched by the domain controller from replication partners to ensure that the Active Directory is up to date and accurate. Whenever there is data loss or corruption in the Active Directory this method is used (default).
Let us move to the next Windows Server Interview Questions
8. Authoritative Restore of Active Directory?
Answer:
The second step after a non-authoritative restore is an authoritative restore process. One of the key features of authoritative restore is that it can increment the version numbers of the attributes or an object in an entire directory. This type of restore is used to restore a single deleted user/object. There will be a mismatch in the version numbers and hence care must be taken while restoring using authoritative restore process
9. Explain in windows DNS server What is Primary, Secondary and Stub zone?
Answer:
DNS stands for domain name system, which is used as a reference table to match the domain names to the ip addresses
The below are the three types of zones in Windows DNS server:
- Primary Zone: In the primary zone, the file is saved as a text file with extension being (.dns)
- Secondary Zone: This is a backup for the primary server which acts as load balancing and also provides fault tolerance. This is usually read-only file which is placed in another DNS server
- Stub Zone: This consists of the name server and SOA records which help in reducing the DNS search orders
10. Explain what is the major difference between NTFS (New Technology File System) or FAT (File Allocation Table) on a local server?
Answer:
The major differences between FAT32 and NTFS are as below:
| Feature | FAT32 | NTFS |
| Maximum file name | 8.3 Characters | 255 characters |
| Maximum file size | 4GB | 16TB |
| File/Folder Encryption | No | Yes |
| Fault Tolerance | No | Auto Repair |
| Security | Only Network | Local and network |
| Compression | No | Yes |
| Conversion | Possible | Not allowed |
| Compatibility | Win 95/98/2k/2k3/XP | Win NT/2K/XP/Vista/7 |
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to List Of Windows Server Interview Questions and Answers. Here we have covered the few commonly asked interview questions with their detailed answers so that candidates can crack interviews with ease. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –