Updated November 28, 2023
Introduction to Windows Tools and Utilities
In the ever-evolving landscape of computing, Windows operating systems have maintained their prominence, offering a robust platform for users across the globe. Beyond the familiar interface and user-friendly environment, Windows has a suite of powerful tools and utilities designed to enhance performance, security, and overall user experience. This article delves into the essential Windows tools and utilities, providing users with a comprehensive guide to optimize their system, troubleshoot issues, and leverage additional features for increased productivity.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Importance
- System Maintenance Tools
- Security Tools
- Performance Optimization Tools in Windows
- Security Utilities
- System Management Utilities
- Troubleshooting Utilities
- Additional Tools and Utilities in Windows
Importance of Windows Tools and Utilities
In the vast digital landscape of Windows operating systems, tools, and utilities play a pivotal role in shaping the user experience. These tools are not mere add-ons but form the backbone of system management, security, and optimization. Understanding the importance of these tools is key to harnessing the full potential of your Windows environment. Here’s a closer look at why these tools matter:
1. System Maintenance and Optimization:
- Efficient Resource Utilization: Tools like Disk Cleanup and Disk Defragmenter ensure your system operates smoothly by eliminating unnecessary files and organizing data for optimal performance.
- Task Management: The Task Manager allows users to monitor and control running processes, ensuring system resources are allocated efficiently.
2. Security Enhancement:
- Built-in Protection: Windows Defender, BitLocker, and Windows Firewall provide essential security features, safeguarding your system against malware, unauthorized access, and network threats.
- Regular Updates: Windows Update keeps your operating system current, delivering critical security patches and bug fixes to protect against emerging threats.
3. Performance Monitoring and Troubleshooting:
- Real-time Insights: Tools like Task Manager and Resource Monitor offer real-time insights into system performance, helping users identify and address issues promptly.
- Diagnostic Capabilities: Event Viewer and Reliability Monitor enable users to diagnose and troubleshoot system errors, ensuring a more stable computing environment.
4. User Productivity:
- Remote Access: Utilities like Remote Desktop Connection empower users to access their systems remotely, fostering collaboration and troubleshooting opportunities.
- Screenshot Tools: Snipping Tool or Snip & Sketch enhances communication by allowing users to capture and annotate screenshots easily.
5. Data Security and Privacy:
- Disk Encryption: BitLocker encrypts entire disk volumes, ensuring sensitive data confidentiality and protection against unauthorized access in case of theft or loss.
- Firewall Protection: Windows Firewall acts as a barrier against unauthorized network access, preserving the integrity of your system.
6. Customization and Accessibility:
- Startup Management: Tools like MSConfig enable users to customize their startup programs, tailoring the system to their specific needs and preferences.
- Accessibility Features: Windows utilities often include features designed to enhance accessibility, catering to a diverse user base with different needs.
System Maintenance Tools
Efficient system maintenance is paramount to ensuring a smooth and responsive computing experience. Windows provides various built-in tools to streamline maintenance, optimizing your system’s performance and longevity.
Let’s explore these essential system maintenance tools:
1. Disk Cleanup
Over time, your system accumulates unnecessary files, saving valuable disk space. Disk Cleanup is your go-to tool for reclaiming storage by removing files you no longer need. From temporary files to system-created cache, Disk Cleanup targets various categories. Regular usage of this tool helps prevent your disk from becoming bloated, keeping your system responsive.
Purpose: To free up disk space by removing unnecessary files.
Key Features:
- Removes temporary files, system cache, and other redundant data.
- Allows users to select specific categories of files to clean.
How to Use:
- Press the Windows key and S simultaneously.
- Search for “Disk Cleanup” and select the app.
- Choose the drive you want to clean up and press “OK.”
- Select the types of files that you want to delete and press “OK” to start cleaning up your drive.
2. Disk Defragmenter
As you use your computer, files can become scattered across the hard drive, leading to longer load times. Disk Defragmenter adds order to this chaos by rearranging fragmented files, resulting in quicker access to data. While modern Windows versions often perform this task automatically, checking in on Disk Defragmenter occasionally can ensure your system maintains peak performance.
Purpose: To optimize the arrangement of files on a hard drive for faster access.
Key Features:
- Reorganizes fragmented data to improve disk performance.
- Automatically runs on a scheduled basis in newer Windows versions.
How to Use:
- Press Win + S, type “Defragment,” and select “Defragment and Optimize Drives.”
- Choose the drive and click “Optimize.”
3. Windows Update
Security is a top priority, and Windows Update is your shield. Regularly updating your operating system is paramount for safeguarding against evolving threats. Windows Update patches security vulnerabilities and introduces enhancements and fixes for a more stable and reliable computing environment.
Purpose: Maintaining the operating system with the most recent security patches and improvements.
Key Features:
- Provides regular updates for Windows security and performance.
- Allows users to schedule updates for convenience.
How to Use:
- Go to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update.
- To update your device, select “Check for updates” and follow the instructions on the screen
Security Tools
Ensuring the security of your Windows system is paramount in today’s digital landscape. Windows has a range of built-in security tools designed to protect your system from various threats.
Let’s explore these tools and how to leverage them for a more secure computing experience:
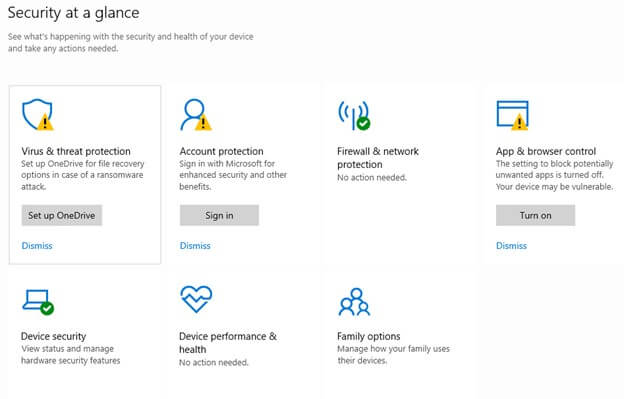
1. Windows Defender
In the realm of cybersecurity, having a reliable antivirus solution is non-negotiable. Integrated seamlessly into the Windows operating system, Windows Defender is the first defense against malicious software. Regular scans and real-time protection protect your system from evolving threats.
Purpose: Windows Defender is Microsoft’s built-in antivirus and anti-malware solution, providing real-time protection against threats.
How to Use:
- Open Windows Security by searching for it in the Start menu.
- Click “Virus & threat protection” and run a quick or full scan.
- Ensure real-time protection is enabled for ongoing security.
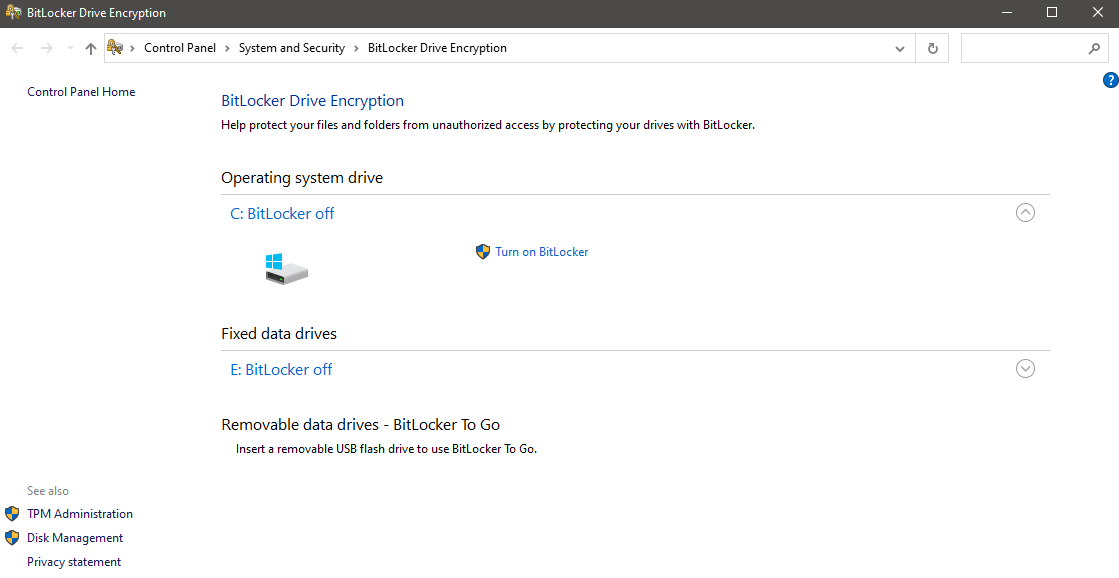
2. BitLocker
The confidentiality of your data is of utmost importance. BitLocker steps in as your guardian by encrypting entire disk volumes, making it challenging for unauthorized users to access sensitive information. Whether using a personal computer or managing devices within an organization, BitLocker provides an additional layer of security against data breaches.
Purpose: BitLocker is a disk encryption program that protects the integrity of your data by encrypting entire disk volumes.
How to Use:
- Search “BitLocker” in the Start menu and select “Manage BitLocker.”
- Follow the instructions to enable BitLocker on your desired drive.
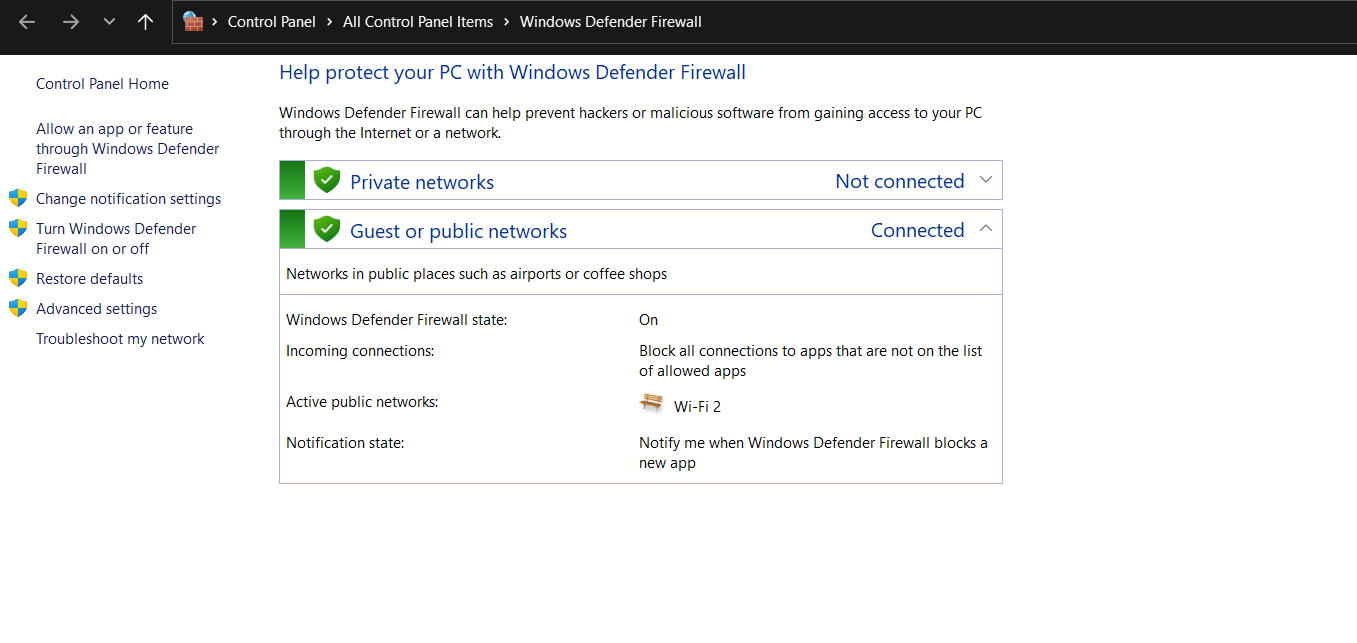
3. Windows Firewall
In the interconnected world of the internet, Windows Firewall acts as a digital gatekeeper. It regulates both inbound and outbound network traffic to prevent unauthorized access to the system. Configuring firewall settings based on your network profile ensures a tailored security approach.
Purpose: Windows Firewall acts as a barrier between your computer and potential threats from the internet, controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic.
How to Use:
- Access Windows Security and click on “Firewall & network protection.”
- Choose the network profile (public or private) and manage firewall settings accordingly.
Performance Optimization Tools in Windows
Ensuring optimal performance of your Windows system is critical for a smooth computing experience. Windows provides built-in tools for monitoring, managing, and optimizing system performance. Let’s explore these performance optimization tools in detail:
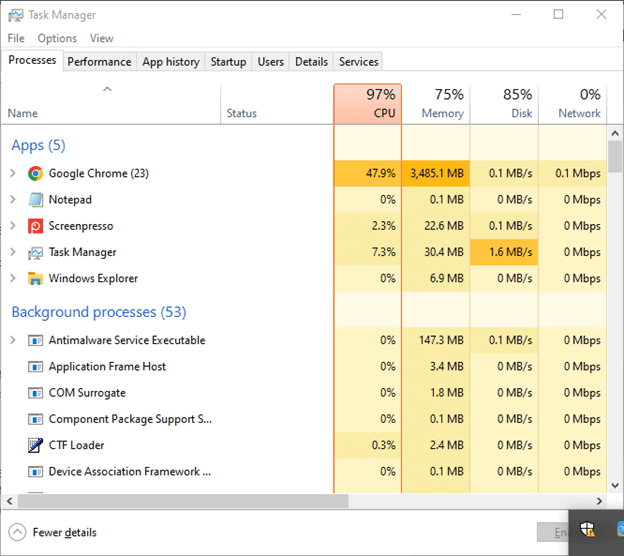
1. Task Manager
Task Manager is your backstage pass in the ever-evolving dance of processes and applications. Offering real-time insights allows you to monitor and manage running processes, ensuring your system resources are allocated efficiently. From identifying resource-hungry applications to managing startup programs, Task Manager puts you in control.
Purpose: Task Manager provides real-time insights into running processes, system performance, and resource utilization.
How to Use:
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc or Ctrl + Alt + Del and select “Task Manager.”
- Explore tabs such as “Processes,” “Performance,” and “Startup” to manage tasks and view system statistics.
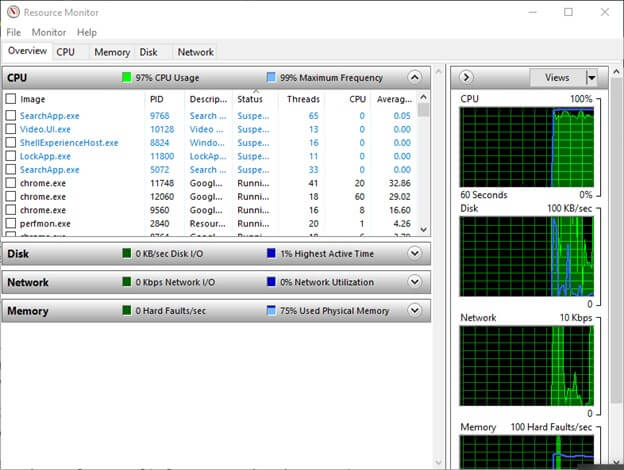
2. Resource Monitor
Resource Monitor takes a more granular view of resource utilization into the spotlight. Whether it’s CPU, memory, disk, or network activity, this tool provides detailed information to help you identify potential bottlenecks. With this knowledge, you can optimize your system for a smoother performance.
Purpose: Resource Monitor looks at how your system resources, including CPU, memory, disk, and network, are used.
How to Use:
- To open the Resource Monitor, search for it in the Start menu.
- Navigate through the tabs to analyze resource usage and identify potential bottlenecks.
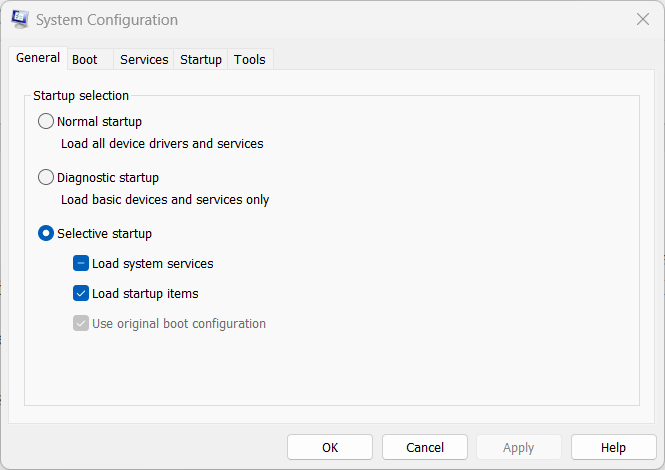
3. MSConfig (System Configuration)
As your system boots up, unnecessary startup programs can contribute to sluggish performance. MSConfig, short for System Configuration, empowers you to manage these startup applications. Selectively enabling or disabling programs can tailor your system startup to focus on essentials, reducing boot times and improving overall responsiveness.
Purpose: MSConfig allows you to manage startup programs, services, and boot options, optimizing system boot times.
How to Use:
- To open the Run dialog, press Windows + R simultaneously. After opening the dialog box, type “msconfig” and press Enter key to execute the command.
- Explore the “Startup” tab to enable or disable startup programs, improving overall system performance.
Security Utilities
Beyond the built-in security tools, Windows also offers additional utilities that provide advanced features and functionalities to enhance your system’s overall security. Let’s delve into these security utilities and explore how they contribute to a robust defense against potential threats:
1. Windows Security (previously Windows Defender Security Center)
As the control center for your system’s security, Windows Security combines antivirus, firewall, and various protection features under one roof. This centralized hub allows you to manage your security settings efficiently, protecting your system against evolving threats.
Purpose: Windows Security consolidates various security features, including antivirus, firewall, device security, and more, in a centralized hub.
How to Use:
- Open Windows Security from the Start menu.
- Explore different sections to manage and customize your security settings.
2. Microsoft Safety Scanner
The Microsoft Safety Scanner comes to the rescue when you suspect malware on your system. This standalone tool is designed for on-demand scanning and removal of malicious software, providing an extra layer of defense against potential threats that might have slipped through real-time protection.
Purpose: Microsoft Safety Scanner is a standalone tool that helps remove malware, spyware, and other malicious software.
How to Use:
- Download and run Microsoft Safety Scanner from the official Microsoft website.
- Follow on-screen instructions to perform a scan and remove threats.
3. Windows Defender Offline
Windows Defender Offline seeks particularly resilient threats that may hide or operate at a deeper level. By running a scan outside of the Windows environment, this utility ensures a thorough examination and removal of malware, enhancing your system’s resilience against sophisticated attacks.
Purpose: Windows Defender Offline allows you to run a scan and remove malware outside the Windows environment, which can be helpful in more stubborn threats.
How to Use:
- Search “Windows Security” in the Start menu and select “Virus & Threat Protection.”
- Under “Current threats,” select “Scan options” and choose “Windows Defender Offline scan.”
System Management Utilities
Efficient system management is crucial for maintaining a well-functioning and organized computing environment. Windows provides a set of utilities that allow users to manage various aspects of their systems, from user accounts to device drivers.
Let’s explore these system management utilities in detail:
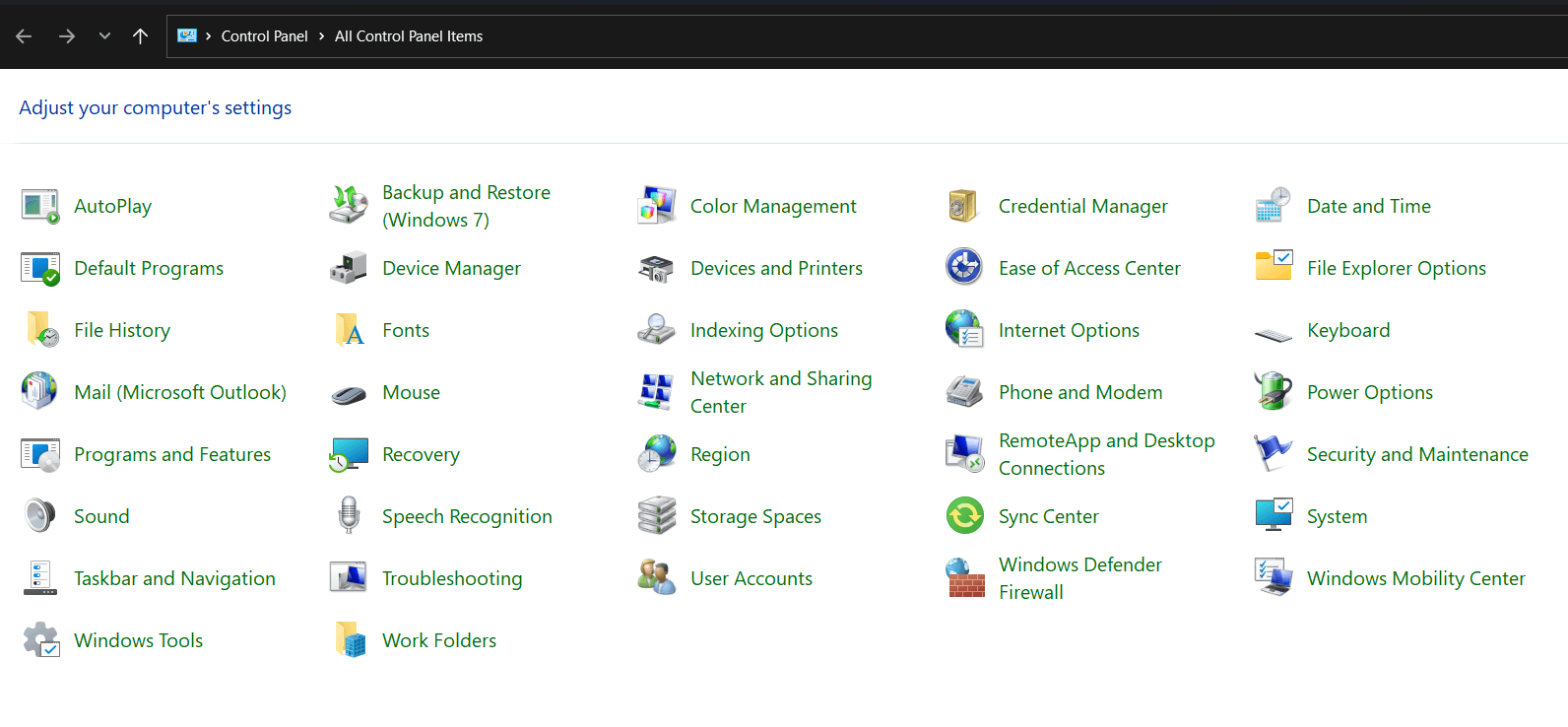
1. Control Panel
Control Panel remains a cornerstone of Windows system management, offering a centralized location for configuring many settings. From adjusting the desktop appearance to managing user accounts, the Control Panel empowers users to tailor their system to their preferences.
- Centralized Settings: The Control Panel is the centralized hub for configuring system settings, managing hardware, and adjusting security and privacy options.
- User Account Management: Control Panel allows users to create and manage user accounts, control password policies, and configure parental controls.
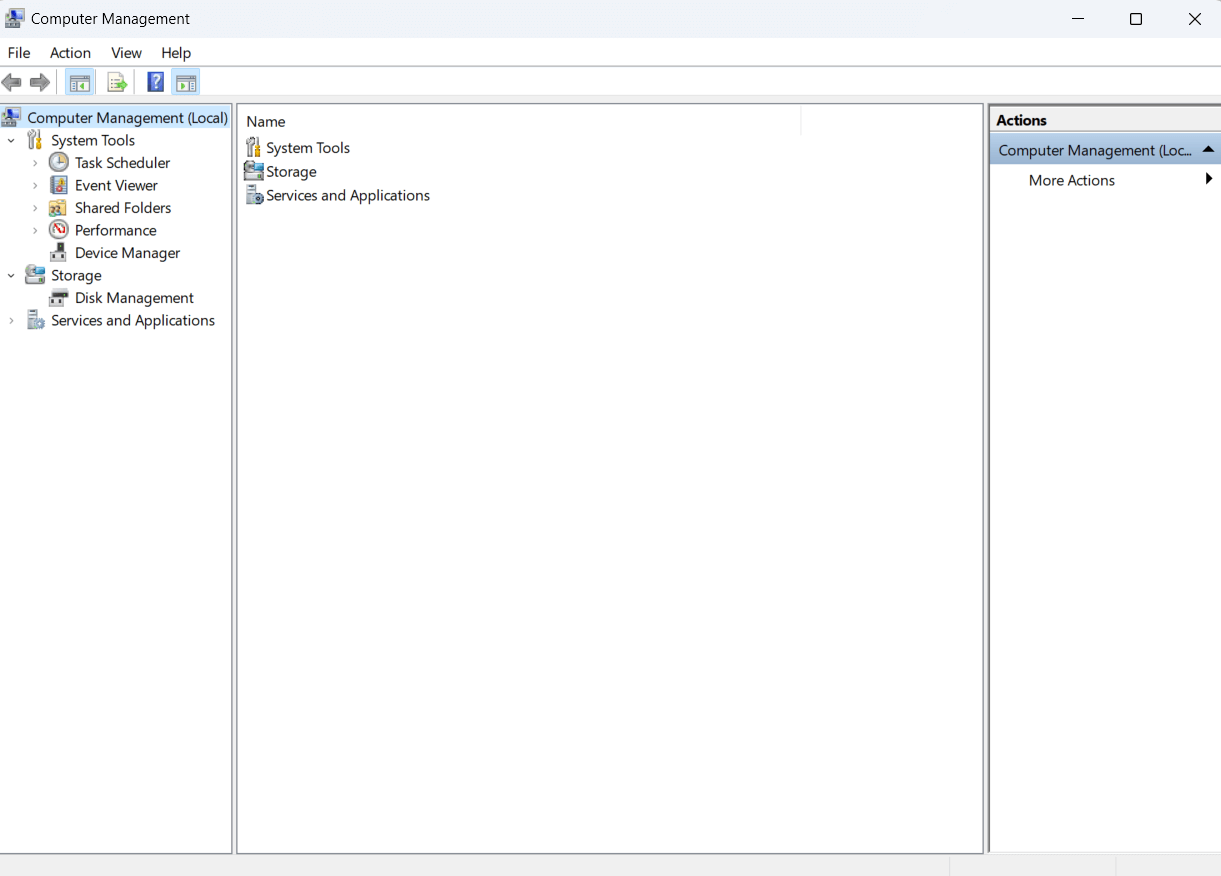
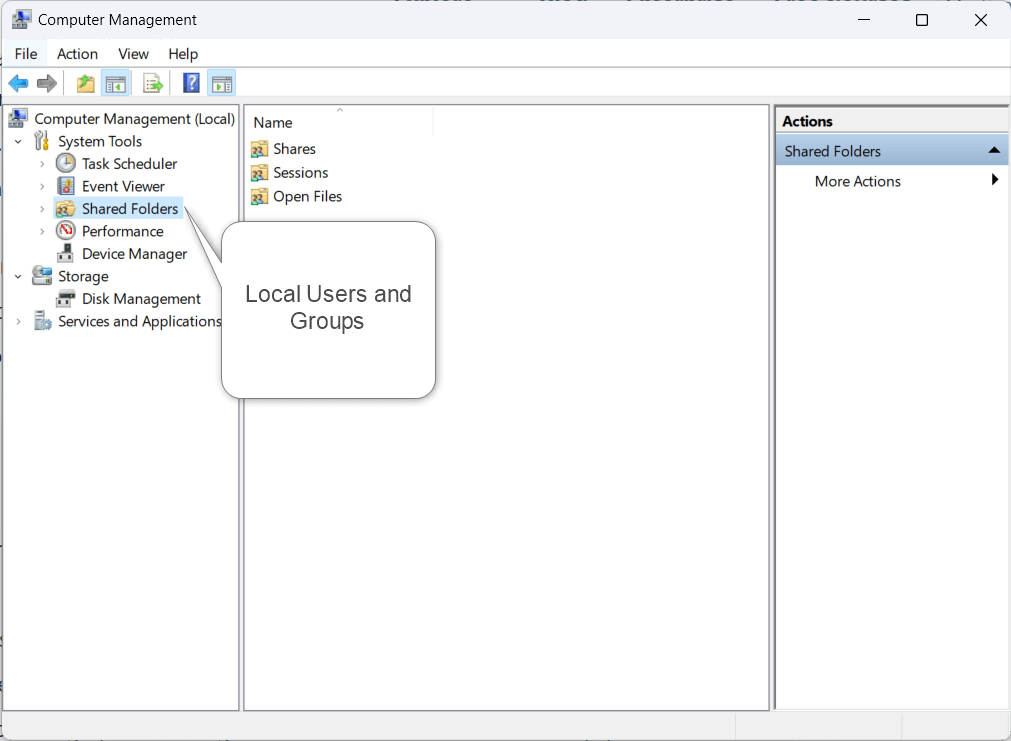
2. Computer Management
For more advanced system management tasks, Computer Management is the go-to utility. With tools like Device Manager, Disk Management, and Event Viewer, administrators can efficiently handle tasks ranging from hardware management to system event analysis, all within a single interface.
- Comprehensive Toolset: Computer Management offers a complete set of tools for system administrators, including Device Manager, Event Viewer, Disk Management, and more.
- System Services: Manage system services, view system events, and control device configurations from a single interface.
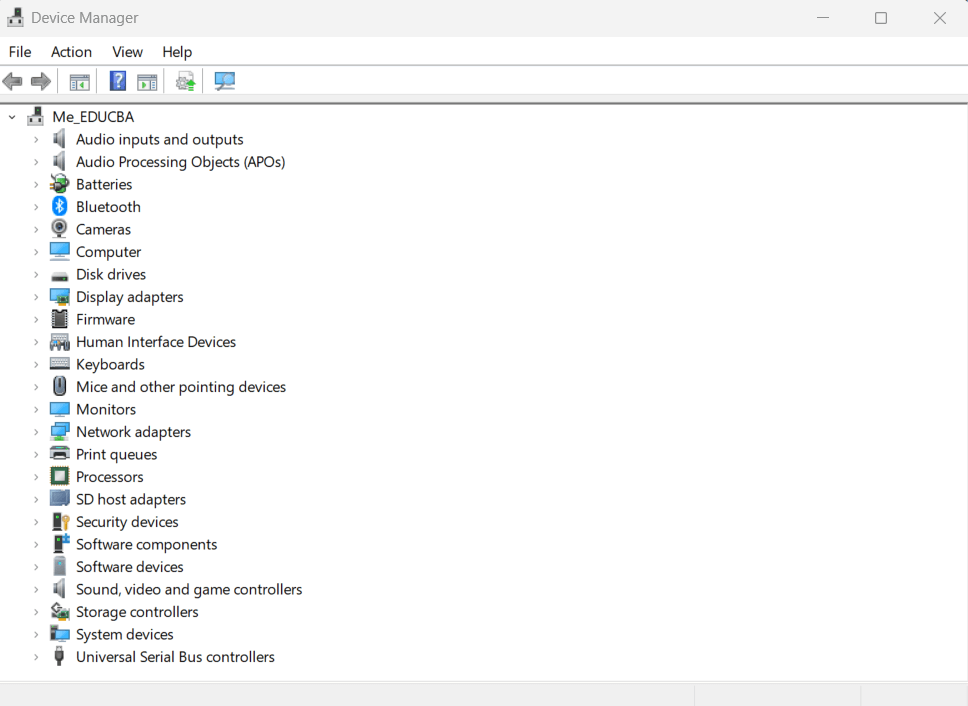
3. Device Manager
Managing hardware devices is simplified through Device Manager. Whether it’s updating drivers, troubleshooting device conflicts, or controlling hardware settings, Device Manager ensures that your system’s hardware components work in harmony.
- Hardware Management: Device Manager lets users view and manage hardware devices installed on their systems.
- Driver Updates: Update, roll back, or uninstall device drivers, ensuring hardware compatibility and stability.
4. Local Users and Groups
User account management is a critical aspect of system administration. Local Users and Groups provide administrators with the tools to create, modify, and organize user accounts and groups, contributing to a secure and well-organized computing environment.
- User and Group Management: This utility allows administrators to manage local user accounts, groups, and memberships.
- Access Control: Control access permissions and assign users to specific groups for streamlined system management.
Troubleshooting Utilities
When issues arise within your Windows system, the right tools are essential for efficient problem resolution. Windows provides a range of troubleshooting utilities to help users diagnose and address various system-related challenges.
Let’s explore these utilities and their functions:
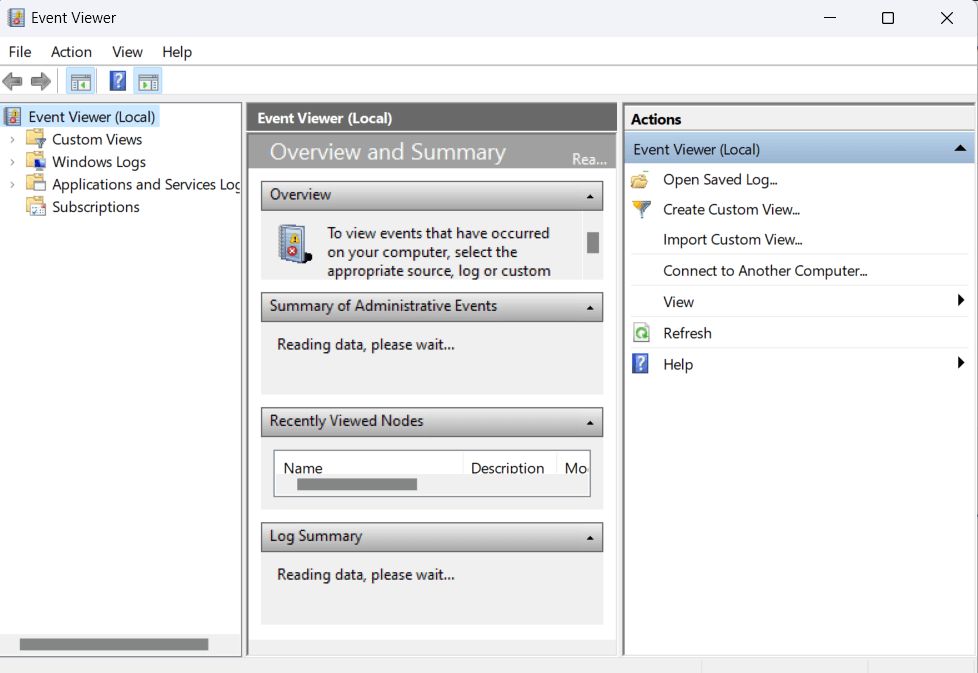
1. Event Viewer
Event Viewer acts as a detective’s notebook when mysterious errors or unexpected behaviors occur. Logging a wide array of system events, Event Viewer provides invaluable insights into what happened, where, and why. Understanding these logs is crucial for effective troubleshooting.
- System Logs: Event Viewer logs events and errors on your system, providing valuable information for troubleshooting.
- Filtering Options: Filter logs based on event type, source, or time to pinpoint specific issues.
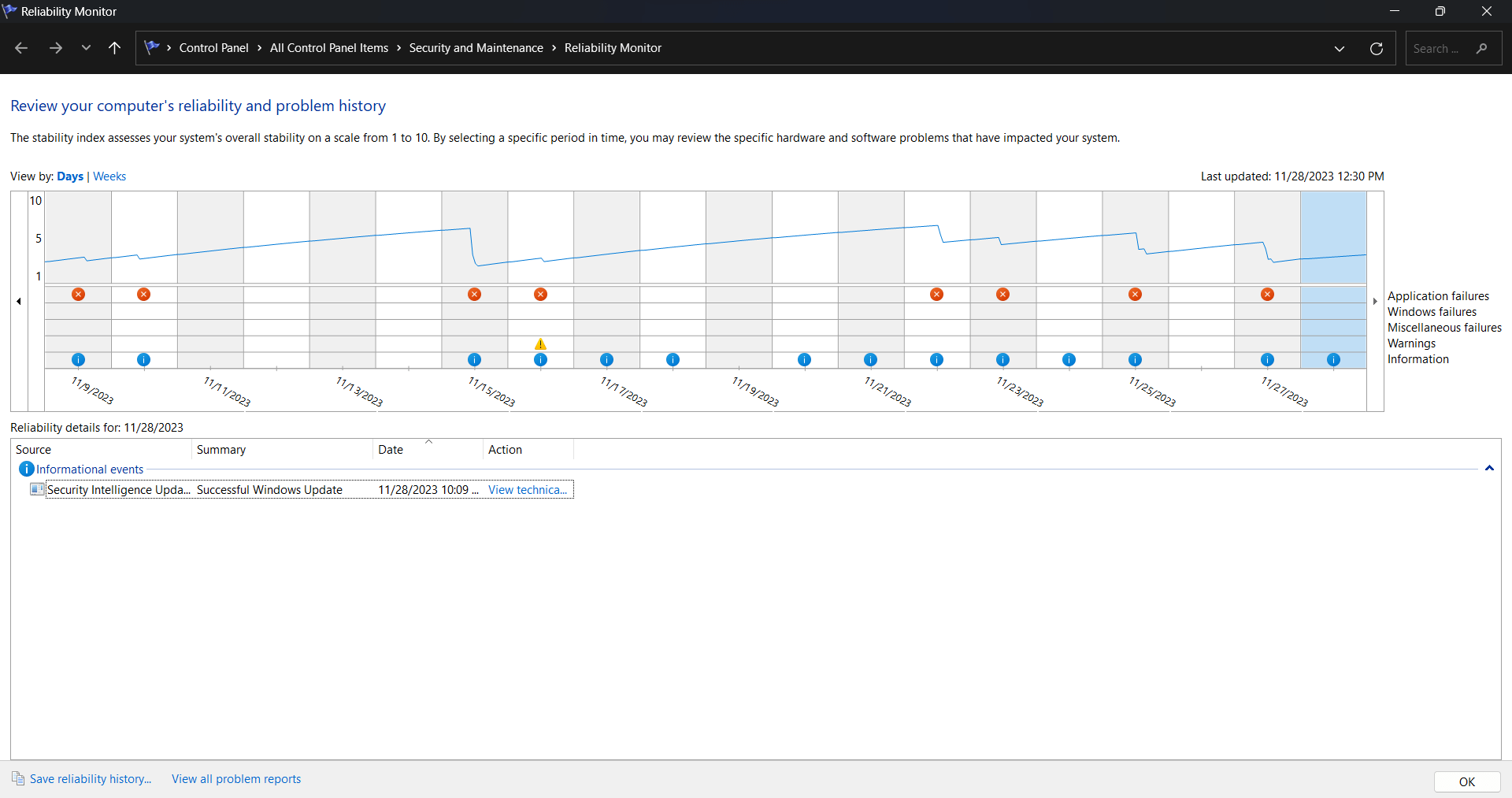
2. Reliability Monitor
For a holistic view of system stability over time, Reliability Monitor shines. It presents a timeline of critical events, errors, and application installations, helping users identify patterns and potential triggers for issues. With this information, troubleshooting becomes a more targeted and effective process.
- Timeline of Events: Reliability Monitor offers a timeline of system events, errors, and application installations, aiding in identifying patterns.
- Critical Events: Critical events are highlighted, allowing users to focus on issues that may impact system stability.
3. System Configuration (MSConfig)
Startup-related problems can be a common source of frustration. MSConfig comes to the rescue by allowing users to manage startup programs. Users can identify and eliminate issues hindering a smooth startup experience by selectively enabling or disabling items.
- Startup Management: MSConfig helps manage programs that launch at startup, allowing users to identify and disable potential culprits causing system issues.
- Diagnostic Startup: Enable diagnostic startup to troubleshoot startup-related problems.
4. Troubleshooters
Windows Troubleshooters are like digital problem-solving companions. These built-in wizards address specific issues, providing step-by-step guidance to identify and resolve common problems. From network connectivity to hardware glitches, troubleshooters simplify the resolution process.
- Built-in Wizards: Windows includes troubleshooters for common issues, such as network problems, hardware and devices, and Windows Update.
- Step-by-Step Guidance: Troubleshooters guide users through steps to identify and resolve specific issues.
Additional Tools and Utilities in Windows
Beyond the core system management, security, and troubleshooting utilities, Windows offers additional tools and applications designed to cater to specific tasks and enhance user productivity.
Let’s explore some of these additional tools and their functionalities:
1. Snipping Tool/Snip & Sketch
In the realm of visual communication, these tools are your digital cameras. Snipping Tool and Snip & Sketch allow users to capture screenshots, annotate images, and highlight important sections. Whether for sharing information or documenting steps, these tools offer versatility in capturing moments on your screen.
- Screenshot Capture: These tools allow users to capture and annotate screenshots, facilitating communication and documentation.
- Annotation Tools: Add highlights, annotations, and freehand drawings to captured screenshots.
2. Remote Desktop Connection
Remote Desktop Connection breaks physical barriers by enabling users to access and control remote computers. This tool fosters connectivity and convenience for tech support or collaborative work. Seamlessly interact with a remote system as if you were seated in front of it.
- Remote Access: This tool enables users to connect to remote computers over a network or the internet, fostering collaboration and troubleshooting opportunities.
- Control and Access: Access and control a remote computer as if you were physically present at that location.
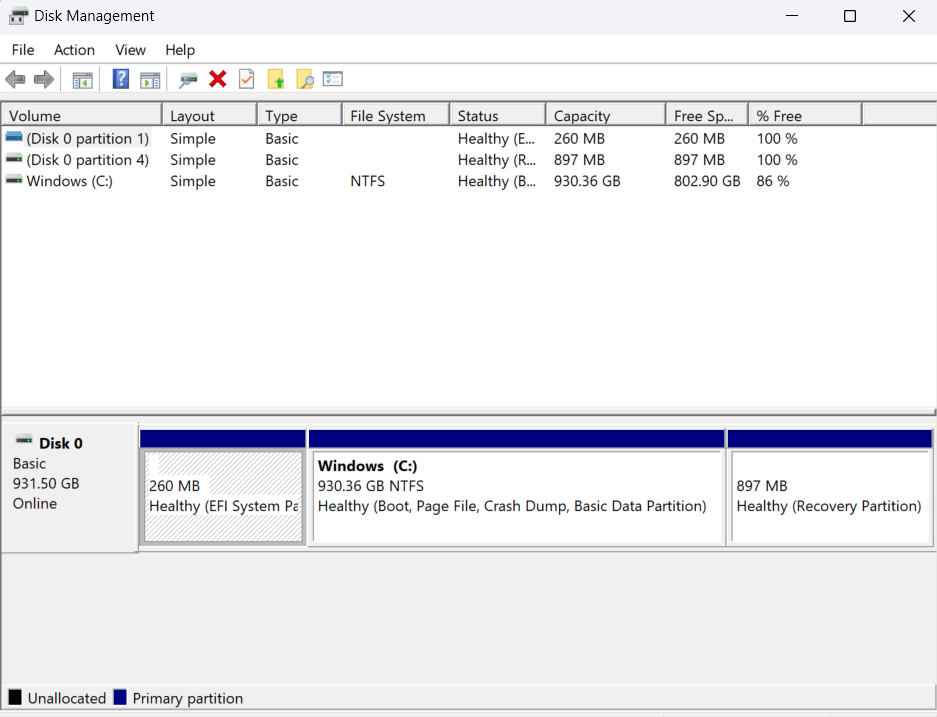
3. Disk Management
Managing disk partitions and volumes is made simple with Disk Management. Whether you need to create, delete, or resize partitions, this tool provides the necessary controls for efficient data organization. Monitor disk health and optimize storage allocation for better system performance.
- Partition Management: Disk Management facilitates the creation, deletion, and resizing of disk partitions on your system.
- Drive Health Monitoring: Check disk status and manage volumes for efficient data storage.
4. Task Scheduler
Task Scheduler acts as your personal assistant, automating routine tasks at specified intervals or triggering them based on specific events. From system maintenance to running scripts or applications, this tool allows you to set and forget it, saving time and streamlining processes.
- Automated Tasks: Task Scheduler enables users to schedule automated tasks at set times or in response to specific events.
- System Automation: Automate system maintenance, backups, and application launches for increased efficiency.
5. Character Map
Sometimes, the keyboard might fall short when you need special characters or symbols. Character Map comes to the rescue, offering an array of characters from different languages and character sets. It’s a visual library of characters that might need to be more readily available through standard typing.
- Special Characters: Character Map provides a visual interface to access special characters and symbols that might not be readily available on the keyboard.
- Unicode Support: Explore and insert characters from various languages and character sets.
Conclusion
Windows tools and utilities are essential for a secure, efficient, and well-managed computing experience. These built-in utilities allow users to customize their environments, from system maintenance to security, performance optimization, and more. By leveraging these tools, users can improve productivity, troubleshoot issues, and unlock the full potential of their Windows operating system. Using the diverse toolkit available to enjoy a seamless Windows experience is important.
Recommended Articles
We hope this EDUCBA information on “Windows Tools and Utilities” benefited you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.