Updated July 14, 2023

What is the Written Down Value Method?
The written-down value method is a method of depreciation wherein there is the application of constant depreciation rate on the ending balance of the tangible asset or on the net book value corresponding to the tangible asset wherein maximum depreciation is recorded at early years of the asset and reduced depreciation at later years of the asset life.
This technique enables the business to identify depreciation expense systematically, which further helps the organization identify the expense of depreciation at the very initial stage of useful life.
Explanation
In the accounting concept, several methodologies apply to matching expenses as and when incurred with the revenues generated by the business on a similar timeline or the same application period. To align with this concept, the business determines depreciation or amortization. The organizations employ depreciation on the physical, tangible assets and amortization on the intangible assets such as goodwill, software, and patents. Such a method enables the business to expense the economic value out of the tangible assets over a longer time frame.
The organization does not deduct the full amount of the purchase of the tangible asset from the net income; rather, they transfer the costs on many different accounting financial periods. The written-down method is employed in the determination of the effective value of the asset by deducting the accumulated depreciation or amortization from the beginning balance of the asset.
How Does It Work?
The written-down method assumes that some type of asset has a limited life and has to be depreciated with a higher rate of depreciation over the course of the asset’s useful life. The method is also applicable for those assets requiring higher maintenance and where the business has to incur high repair costs on such assets. Therefore, this method helps reflect the true value of the asset on the balance sheet. Therefore, under this method, the business has to note down the beginning balance of the asset. The next step would involve determining depreciation expense at the rate prescribed for the fixed assets.
The depreciation expense would be deducted from the beginning balance to arrive at the ending balance of the asset. The asset’s ending balance would be the asset’s beginning balance for the next useful year. Hence, a similar exercise would be performed to arrive at the depreciation expense applicable through the asset’s useful life.
Examples of Written Down Value Method (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation of the Written Down Value Method in a better manner.
Example #1
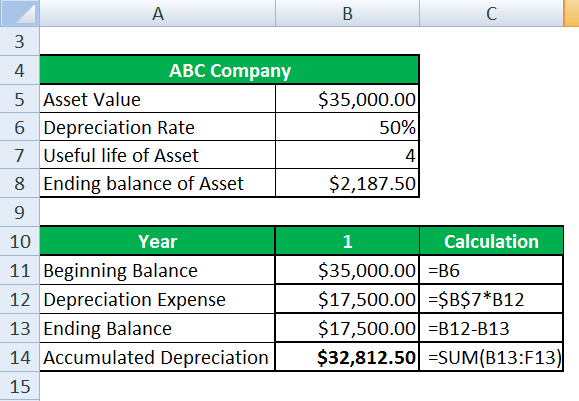
Let us take the example of ABC Company. The business purchased the asset for $35,000, and the business depreciates the asset at the rate of 50 percent annually. The asset has a useful life of four years. Help the management arrive at the effective value of the asset at the end of its useful life.
Solution:
| ABC Company | |
| Asset Value | $35,000.00 |
| Depreciation Rate | 50% |
| The useful life of Asset | 4 |
| Ending balance of Asset | $2,187.50 |
Written Down Value Method is calculated as
For Year 1
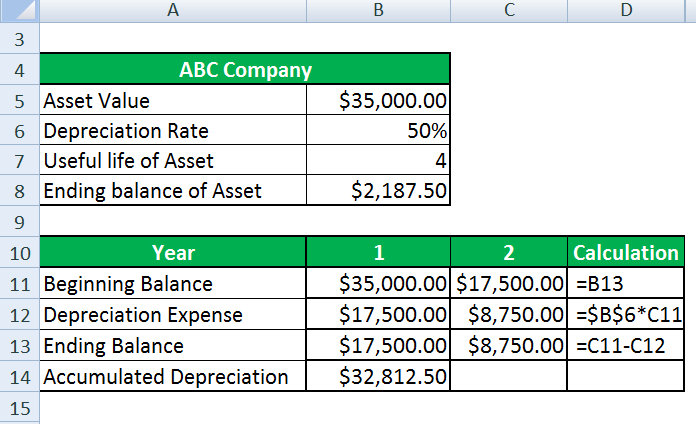
For Year 2
Similarly calculated for 3 and 4 years.
The following table displays the applicable depreciation expense through the period and the effective value of the asset: –
Importance of the Written Down Value Method
The written-down method of depreciation is the best applicable method for computing depreciation expense whenever the asset faces a risk of obsolescence and getting quickly outdated in the market as it provides the organization with the asset’s fair market value once the asset has exhausted its useful life and has become obsolete. This is the correct method for arriving at the expenses that match the level of revenues as the asset provides utility in the early years of its useful life and similarly reduced utility at the later stage of the useful life of the asset and under such a scenario high depreciation expense is charged which is later reduced to lower levels at the later stage of the useful life of the asset.
Advantages
Some of the advantages are given below:
- This method helps in the computation of depreciated value of the tangible asset. This information helps the management determine the effective price at which the asset can be liquidated.
- The method broadly applies the higher amount on the depreciation for the early stage in the asset’s useful life.
- It is one of the correct methods or approaches for recording depreciation on assets that lose their values quickly. The written-down method is applied to the software developed by the technological business. This enables the business to recognize the asset’s fair market value on the balance sheet as and when technology becomes obsolete.
- Recording the depreciation expense’s higher value in the asset’s early life results in lesser taxes. This method helps the organization defer its tax liability. It provides businesses with appreciated cash profits and lower levels of net income. The cash profits are appreciated because it is to be noted that the depreciation expense is a non-cash expense.
Disadvantages
Some of the disadvantages are given below:
- The method computes a very high value of the depreciation expense applicable to the net book value of the tangible asset. Hence, replicating such a method on tangible assets that uniformly offer utility throughout their life is impossible.
- Hence, assets with the least risk of being outdated and experiencing obsolescence and technological change cannot replicate or apply this method.
- The higher value of depreciation reported on the income statement results in reduced net income levels and a bad-looking bottom line.
Conclusion
The written-down value depreciation method is a method that applies depreciation at a higher rate in the initial years and lower depreciation rates at the ending years of the useful life of the asset. The method is also termed the declining and diminishing balance methods. Such a method should be applied to tangible assets with the risk of obsolescence.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Written Down Value Method. Here we also discuss the introduction and how does write-down value method work. Along with advantages and disadvantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –