Introduction to ZBrush brushes
In this article, we are going to learn about ZBrush brushes. There are many different brushes that you can use to sculpt in Zbrush. Each brush has some unique property that allows doing something which other brushes cannot. Brushes can be modified using several controls such as Gravity, Wrap Mode, Density, etc. other than the standard Z intensity and Draw Size but in this article, we will stick to the default configuration. There are also many categories of brushes like clip, curve, planar, trim, InsertMesh, Curve Bridge, Alpha 3D but we are going to focus on sculpting brushes.
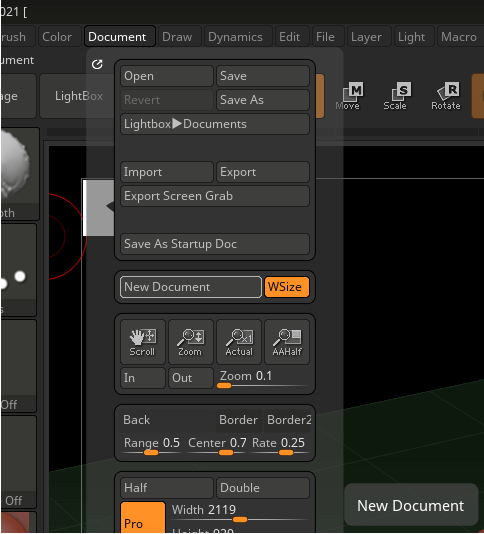
Step 1: Go to Document in the menu bar and then select New document with WSize on which will make the canvas size the same as the viewport size.
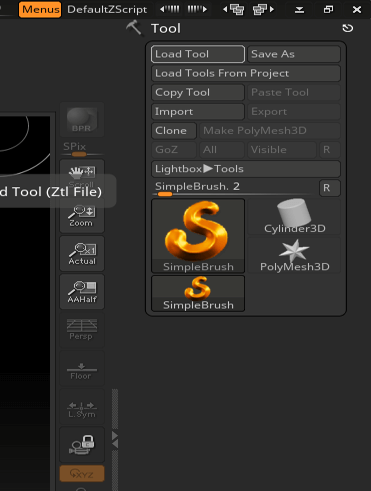
Step 2: Start with A Load tool option.
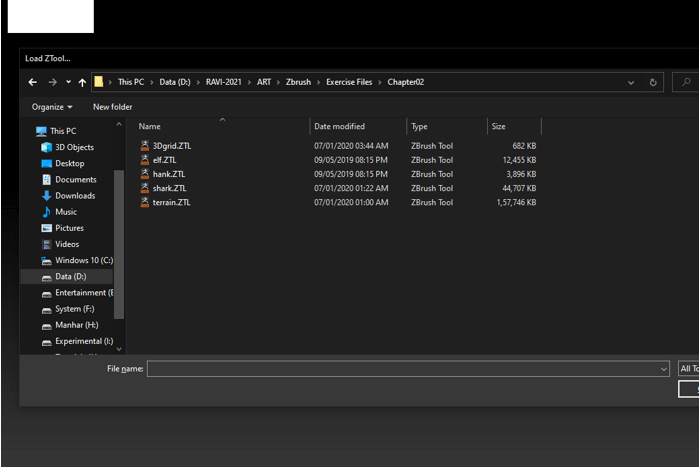
Step 3: Navigate to the stored tool if you have any or you can select some primitive tools like a sphere as this tool will better demonstrate various brushes.
Step 4: Then drag the tool inside the viewport.
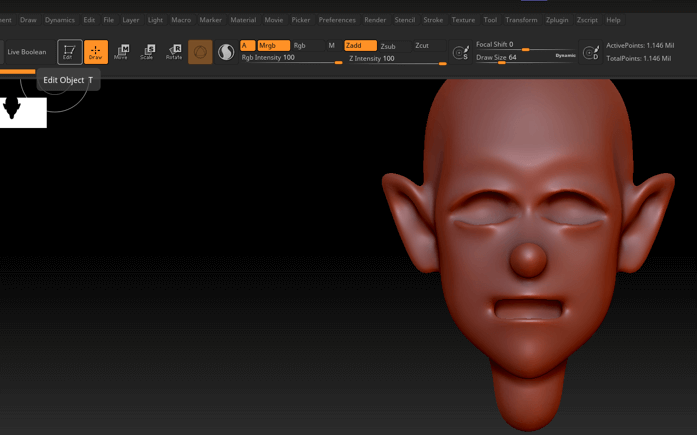
Step 5: After creating the sphere go to edit mode. This mode will allow you to sculpt the 3D object. Also, when you place a primitive 3D object in the edit mode it will automatically be cloned in the tool palette.
Step 6: Enable the perspective button to which will apply perspective foreshortening to a 3D object. Also, press Floor to activate the perspective floor grid which can be activated per axis, and by default, Y-axis is enabled.
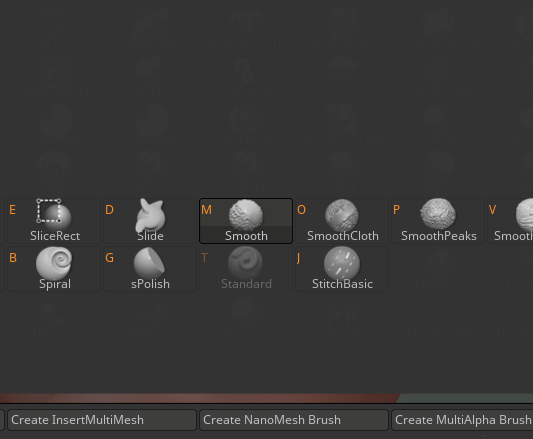
Step 7: Let’s start with the first brush which is Standard. The hotkey to select it is B – S – T.
Step 8: So, the Standard brush is the default brush in Zbrush and it displaces the vertices outward giving an illusion of a clay build-up to a sculpture. Various modifiers such as strokes, alphas, and edit curves can be used with it, and pressing Alt reverses the effect and causes it to carve in instead of build-up. You can adjust Z intensity to adjust how the depth information is applied to the current tool or object and draw size determines the size of brush strokes or editing actions. If you want more fine-tuning, then you can use the focal shift but its uses are rare and it is mostly to control the falloff how steep or shallow you want.
Step 9: Next brush which is Smooth. The hotkey to select it is B – S – M.
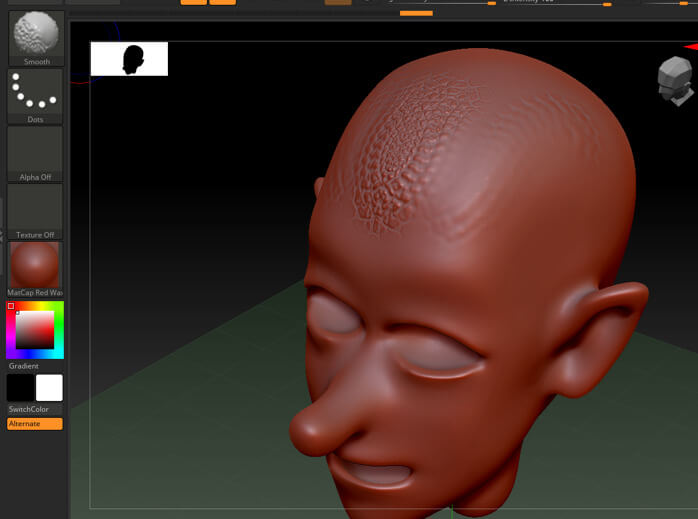
Step 10: Smooth brush first calculates the average level of the surface and then smooth the details accordingly towards an average level.
Step 11: Next brush which is Move. The hotkey to select it is B – M – V.
Step 12: The move tool can be used to make a subtle adjustments and to modify some of the facial features to indicate emotions as well as to get a more natural asymmetric face. Move also ignore some brush modifiers like strokes.
Step 13: Next brush which is Inflate. The hotkey to select it is B – I – N.
Step 14: Inflate use the vertices of geometry and is expanded on their own normal as opposed to standard brush which pulls or pushes the geometry along the center of the brush. This brush is especially useful when displacing a large amount of surface with one or two strokes.
Step 15: Next brush which is Elastic. The hotkey to select it is B – E.
Step 16: The working of Elastic brush is similar to Inflate but for some models, it maintains the original shape of the surface as the displacement of surface happens. You really need to experiment to see which type of brush to use in your specific case.
Step 17: Next brush which is Displace. The hotkey to select it is B – D – I.
Step 18: Displace has the working similar to Inflate brush but the details of the underlying surface are kept intact which suggest there is a swelling in case of humans or displacement in any other model.
Step 19: Next brush is Magnify. The hotkey to select is B – M – A.
Step 20: Magnify brush cause displacement of the surface at the same time the vertices are pushed outside of the surface. The amount of magnification can be controlled by Z intensity.
Step 21: Next brush which is Blob. The hotkey to select it is B – B.
Step 22: Blob Brush is good at creating organic effects quickly. It uniformity depends on the irregularities in the surface as it typically produces short irregular blob. The effect is not apparent if used on smooth surfaces.
Step 23: Next brush which is Pinch. The hotkey to select it is B – P – I.
Step 24: Pinch brush pulls the vertices together and it is like reverse of Magnify brush. It is very useful for clothes or creating wrinkles. Pinch is usually used with a Lazy mouse to achieve ridges that are precise and smooth.
Step 25: Next brush is Flatten. The hotkey to select is B – F – A.
Step 26: Flatten brush as the name suggest makes the surface flat and you can press down parts into planar surface which will lower or raise the surface. The angle of flat surface will be dependent by the area under the center of the brush. You can use this in conjunction with a Smooth surface if the surface is not flat enough to flatten.
Step 27: Next brush is Clay. The hotkey to select it is B – C – L.
Step 28: The main purpose of a clay brush is sculpting using alpha. Though other brushes may be used but may have side effects because of their own purpose while clay brush is intended to be used with alpha without side effect.
Conclusion
In this article, we have learned how to use brushes in Zbrush. Firstly, we have started with loading a tool then we starting working on various brushes and demonstrating their general uses and specific use cases if any. We have also seen the hotkeys for each brush so we can have faster access to that brush.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to ZBrush brushes. Here we discuss the Introduction, Steps to create ZBrush brushes. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –